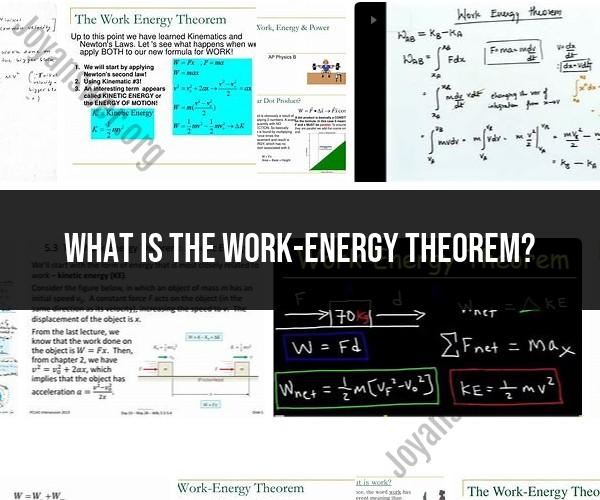
What is the work-energy theorem?
The work-energy theorem is a fundamental principle in physics that relates the work done on an object to the change in its mechanical energy. It essentially states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy.
Mathematically, the work-energy theorem can be expressed as follows:
Where:
- represents the net work done on the object.
- represents the change in the object's kinetic energy.
In this equation, "work" () refers to the mechanical work done on an object by the application of a force. Work is calculated as the product of the force applied to an object and the distance over which the force is applied, in the direction of the force. The formula for calculating work is:
Where:
- is the magnitude of the force applied.
- is the distance over which the force is applied.
- is the angle between the direction of the force and the direction of motion.
"Kinetic energy" () is the energy associated with an object in motion and is given by the formula:
Where:
- is the mass of the object.
- is the velocity of the object.
The work-energy theorem essentially tells us that when a force is applied to an object, and work is done on it, the object's kinetic energy changes. If work is done on the object (positive work), it gains kinetic energy, and if work is done by the object (negative work), it loses kinetic energy. This theorem is particularly useful in analyzing the motion of objects subjected to forces, such as those moving along inclined planes, experiencing friction, or undergoing changes in velocity.
In summary, the work-energy theorem is a fundamental concept that links the concept of work to changes in an object's kinetic energy. It is a valuable tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of objects in various physical scenarios.
The Work-Energy Theorem Demystified: Understanding Its Significance
The work-energy theorem is one of the most fundamental concepts in physics. It states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. In other words, work can be used to change the energy of motion of an object.
The work-energy theorem is significant because it provides a unified understanding of work and energy. It shows that work is a way of transferring energy from one object to another, and that energy can be stored in the form of kinetic energy.
The work-energy theorem has many applications in physics and engineering. It can be used to solve problems involving motion, such as the motion of a projectile or the motion of a car. It can also be used to design machines, such as engines and generators.
Theoretical Foundations: Exploring the Work-Energy Theorem in Physics
The work-energy theorem is based on the following two concepts:
- Work: Work is done on an object when a force acts on the object and the object moves in the direction of the force.
- Kinetic energy: Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
The work-energy theorem can be expressed mathematically as follows:
W = ΔKE
where:
- W is the net work done on the object
- ΔKE is the change in the kinetic energy of the object
The net work is the sum of all the forces acting on the object. The change in kinetic energy is the difference between the final kinetic energy of the object and its initial kinetic energy.
Transforming Forces into Energy: The Work-Energy Theorem Explained
The work-energy theorem can be explained using the following example:
Imagine a ball rolling down a hill. The force of gravity is doing work on the ball. As a result of this work, the ball's kinetic energy increases.
When the ball reaches the bottom of the hill, it stops rolling. The force of gravity is still acting on the ball, but the ball is not moving. This means that the work done by the force of gravity is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the ball.
The work-energy theorem can also be used to explain how machines work. For example, an engine converts the chemical energy in gasoline into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is then used to do work, such as moving a car.
The work-energy theorem is a powerful tool that can be used to understand and solve a wide range of problems in physics and engineering. It is a fundamental concept that is essential for understanding how the world works.