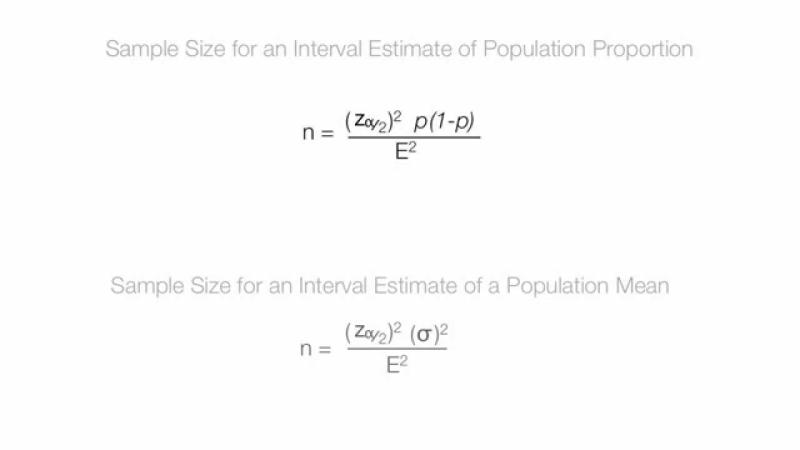
What is the sample proportion formula?
The sample proportion () is a statistic that estimates the proportion of a certain characteristic in a sample. The formula for calculating the sample proportion is:
Where:
- is the sample proportion.
- is the number of occurrences of the characteristic of interest in the sample.
- is the total size of the sample.
The sample proportion is an estimator for the population proportion (), which represents the proportion of the characteristic in the entire population.
It's important to note that the sample proportion is an estimate and can vary from one sample to another. When making inferences about a population based on a sample proportion, confidence intervals or hypothesis tests are often used to account for this variability.
Sure. Here are the answers to your questions:
What is the formula for sample proportion in statistics?
The sample proportion, also known as the empirical proportion, is the number of successes in a sample divided by the total number of observations in the sample. It is an estimate of the population proportion, which is the proportion of successes in the entire population.
The formula for sample proportion is:
p̂ = x / n
where:
p̂is the sample proportionxis the number of successes in the samplenis the total number of observations in the sample
How is the sample proportion calculated?
To calculate the sample proportion, you need to collect data from a sample of the population. The sample should be representative of the population, meaning that it should have the same characteristics as the population. Once you have collected your data, you can count the number of successes in the sample. The success is defined as the event that you are interested in. For example, if you are interested in the proportion of people who like pizza, then the success would be liking pizza. Once you have counted the number of successes, you can divide that number by the total number of observations in the sample. This will give you the sample proportion.
Can you explain the mathematical calculation for sample proportion?
The mathematical calculation for sample proportion is:
p̂ = x / n
where:
p̂is the sample proportionxis the number of successes in the samplenis the total number of observations in the sample
The sample proportion is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion. This means that if you were to collect an infinite number of samples, the average of the sample proportions would be equal to the population proportion. However, the sample proportion is a variable, meaning that it will vary from sample to sample. The amount of variation depends on the sample size. The larger the sample size, the smaller the variation will be.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.