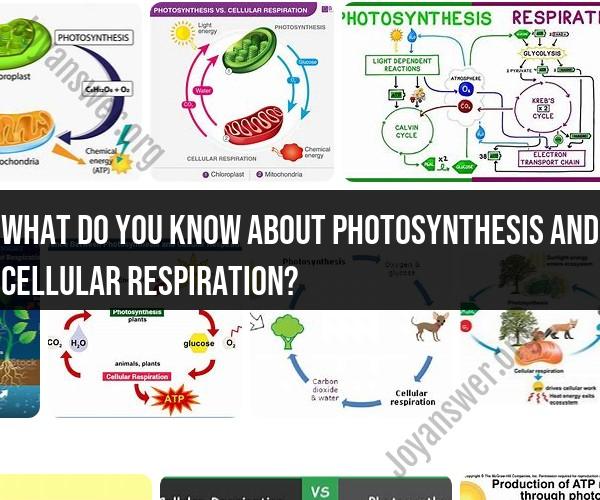
What do you know about photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental and interconnected biological processes that are essential for life on Earth. Here's an overview of each process:
Photosynthesis:
- Location: Photosynthesis primarily occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and some other photosynthetic organisms.
- Function: Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria capture light energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose and other organic molecules.
- Equation: The general equation for photosynthesis is:6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen)
- Products: Oxygen is released as a byproduct, and glucose is used as an energy source and as a building block for other organic compounds.
- Role: Photosynthesis is the foundation of the food chain, providing energy and organic matter to heterotrophic organisms (those that cannot produce their own food).
Cellular Respiration:
- Location: Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria of both plant and animal cells.
- Function: Cellular respiration is a catabolic process that breaks down organic molecules (e.g., glucose) to release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used to power various cellular processes.
- Equation: The general equation for cellular respiration is the reverse of photosynthesis:C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6 O2 (oxygen) → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP
- Products: Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products, and ATP is generated as an energy source.
- Role: Cellular respiration is essential for the survival and functioning of all living organisms. It is the primary way that organisms extract energy from organic compounds.
Interconnection:
- Reciprocal Relationship: These processes are closely interconnected through the exchange of products and reactants. The oxygen produced in photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration, and the carbon dioxide produced in cellular respiration is used in photosynthesis. This interdependence is often described as the carbon cycle.
- Energy Flow: Photosynthesis captures and stores energy from the sun, while cellular respiration releases this stored energy. The energy in glucose produced during photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration to power various cellular functions.
- Sustaining Life: Together, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are integral to the cycling of energy and matter on Earth, supporting life and maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
In summary, photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected processes that play vital roles in the exchange of energy and matter in the biosphere. They are fundamental to the survival and functioning of plants, animals, and many microorganisms. The reciprocity of these processes ensures the flow of energy and the recycling of carbon and oxygen in Earth's ecosystems.
Exploring Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: An Overview
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two essential biological processes that are responsible for the transfer of energy and matter through living systems.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other nutrients to produce energy in the form of ATP.
The Chemical Reactions Underlying Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Light-dependent reactions: The light-dependent reactions use sunlight to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen atoms are used to produce NADPH, a molecule that stores energy, and ATP, the energy currency of the cell. The oxygen atoms are released into the atmosphere.
Calvin cycle: The Calvin cycle uses the energy from NADPH and ATP to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
The Metabolic Pathways of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration occurs in four stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis: Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
Krebs cycle: The Krebs cycle is a series of chemical reactions that break down pyruvate into carbon dioxide and water, producing ATP and NADH.
Electron transport chain: The electron transport chain uses the energy from NADH to produce ATP.
Oxidative phosphorylation: Oxidative phosphorylation is the process by which ATP is produced using the energy from the electron transport chain.
Comparing the Products and Reactants of Both Processes
The products and reactants of photosynthesis and cellular respiration are complementary.
Photosynthesis:
- Reactants: Sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide
- Products: Oxygen and glucose
Cellular respiration:
- Reactants: Glucose and oxygen
- Products: Carbon dioxide, water, and ATP
Symbiotic Relationships Between Producers and Consumers
Producers, such as plants, use photosynthesis to produce food for themselves and other organisms. Consumers, such as animals, eat producers to obtain the energy they need to survive.
The symbiotic relationship between producers and consumers is essential for the flow of energy through ecosystems.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two essential biological processes that are responsible for the transfer of energy and matter through living systems. Photosynthesis produces the food and oxygen that are necessary for life on Earth, while cellular respiration provides the energy that organisms need to survive.
The symbiotic relationship between producers and consumers is essential for the flow of energy through ecosystems.