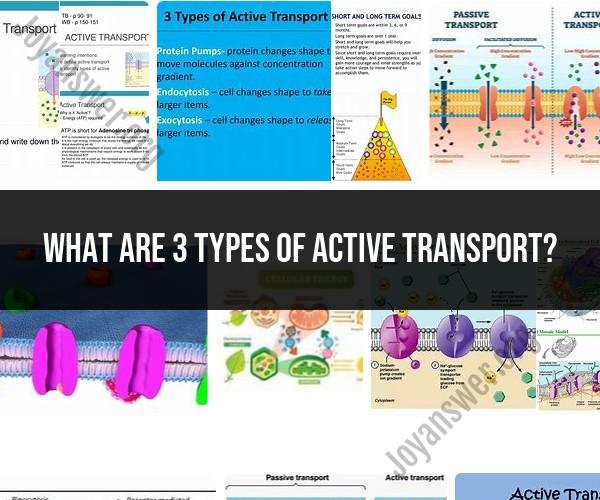
What are 3 types of active transport?
Active transport is a cellular process that moves molecules or ions against their concentration gradient, requiring the expenditure of energy (usually ATP) to achieve this movement. Here are three types of active transport:
Sodium-Potassium Pump (Na+/K+ Pump):
- The sodium-potassium pump is a vital active transport mechanism found in the plasma membranes of animal cells, including nerve cells. It helps maintain the cell's resting membrane potential and is crucial for electrical excitability and nerve signal transmission.
- The pump actively transports three sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and two potassium ions (K+) into the cell against their respective concentration gradients.
- The process involves phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the pump protein, which is coupled with the movement of ions.
Proton Pump (Hydrogen Ion Pump):
- Proton pumps are found in the membranes of various cell types, particularly in the stomach lining and plant cell vacuoles.
- These pumps transport protons (H+) against their concentration gradient. In the stomach, proton pumps are responsible for producing stomach acid (hydrochloric acid), aiding in digestion.
- In plant cells, proton pumps help create a proton gradient across the tonoplast (vacuole membrane), allowing for the uptake of nutrients and maintenance of turgor pressure.
Calcium Pump (Ca2+ Pump):
- Calcium pumps are responsible for actively transporting calcium ions (Ca2+) across cell membranes, often out of the cell or into intracellular organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria.
- These pumps play a crucial role in regulating intracellular calcium levels, which are involved in various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, cell signaling, and neurotransmitter release.
- The calcium pump uses energy to move calcium ions against their concentration gradient.
These active transport mechanisms are essential for maintaining proper cellular functions and the overall homeostasis of organisms. They ensure that specific ions are maintained at appropriate concentrations inside and outside of cells, allowing for various physiological processes to occur.
Active Transport Demystified: Exploring Three Fundamental Types
Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient. This means that the molecules or ions are moving from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Active transport requires energy, which is usually provided by ATP, the cell's energy currency.
There are three fundamental types of active transport:
- Primary active transport: Primary active transport uses energy directly from ATP to move molecules or ions across the cell membrane. An example of primary active transport is the sodium-potassium pump, which moves sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell.
- Secondary active transport: Secondary active transport uses the energy gradient created by primary active transport to move other molecules or ions across the cell membrane. An example of secondary active transport is the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions. Glucose is able to move into the cell against its concentration gradient because it is cotransported with sodium ions, which are moving down their concentration gradient.
- Vesicular transport: Vesicular transport uses vesicles (small sacs) to move molecules or ions across the cell membrane. There are two main types of vesicular transport: exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis is the process of releasing vesicles from the cell. Endocytosis is the process of taking vesicles into the cell.
Cellular Energy and Transport: The Diversity of Active Transport
Active transport is essential for many cellular processes, including:
- Maintaining the cell's internal environment: Active transport helps to maintain the cell's internal environment by regulating the levels of ions and other molecules inside the cell. For example, the sodium-potassium pump helps to maintain the cell's resting membrane potential.
- Absorbing nutrients: Active transport is used to absorb nutrients from the environment. For example, the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions is used to absorb glucose from the intestine.
- Secreting waste products: Active transport is used to secrete waste products from the cell. For example, the sodium-potassium pump is used to secrete hydrogen ions from the cell.
- Transporting molecules within the cell: Active transport is also used to transport molecules within the cell. For example, the Golgi apparatus uses active transport to transport proteins to different parts of the cell.
A Closer Look at Active Transport: Three Key Varieties in Detail
Here is a closer look at the three key varieties of active transport in detail:
Primary active transport:
Primary active transport is the most common type of active transport. It uses energy directly from ATP to move molecules or ions across the cell membrane. An example of primary active transport is the sodium-potassium pump. The sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to move three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell. This creates a concentration gradient for sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane. The concentration gradient for sodium and potassium ions is used to drive other active transport processes, such as the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions.
Secondary active transport:
Secondary active transport uses the energy gradient created by primary active transport to move other molecules or ions across the cell membrane. An example of secondary active transport is the cotransport of glucose and sodium ions. Glucose is able to move into the cell against its concentration gradient because it is cotransported with sodium ions, which are moving down their concentration gradient. The sodium-potassium pump creates the concentration gradient for sodium ions.
Vesicular transport:
Vesicular transport uses vesicles (small sacs) to move molecules or ions across the cell membrane. There are two main types of vesicular transport: exocytosis and endocytosis. Exocytosis is the process of releasing vesicles from the cell. Endocytosis is the process of taking vesicles into the cell.
Exocytosis is used to release molecules from the cell, such as hormones and neurotransmitters. Endocytosis is used to take molecules into the cell, such as nutrients and waste products.
Active transport is a complex and fascinating process. It is essential for many cellular processes, and it plays a vital role in the life of all living organisms.