How is photosynthesis measured?
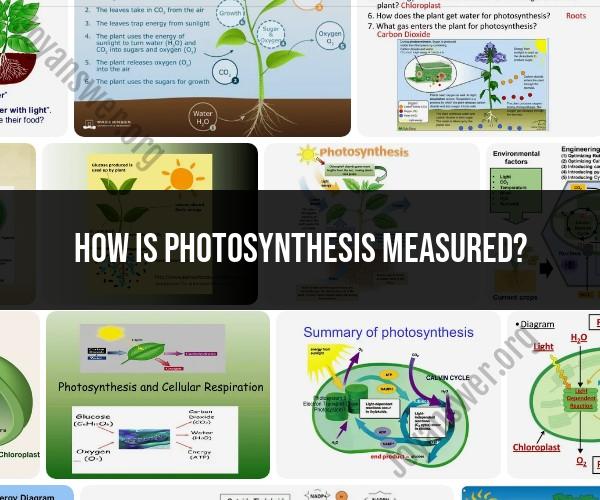
Photosynthesis is a complex biological process that involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose and oxygen. To measure photosynthesis, scientists use various techniques and instruments to assess different aspects of the process. Here are some common methods and techniques used to measure photosynthesis:
Gas Exchange Measurements:
- Oxygen Production: One of the most direct methods for measuring photosynthesis is to monitor the production of oxygen. Oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis, and its release can be measured using an oxygen sensor. The rate of oxygen production is proportional to the rate of photosynthesis.
- Carbon Dioxide Uptake: Photosynthesis involves the uptake of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. By measuring the decrease in CO2 concentration over time, scientists can indirectly determine the rate of photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll Fluorescence:
- Chlorophyll fluorescence measurements provide information about the efficiency of photosynthesis. Chlorophyll molecules emit fluorescence when they absorb excess light energy. By measuring the intensity and duration of this fluorescence, researchers can assess the health and photosynthetic activity of plants.
Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) Sensors:
- PAR sensors measure the intensity of light within the photosynthetically active range (usually 400-700 nm). These sensors help researchers understand how variations in light intensity affect photosynthesis.
Leaf Disc Assay:
- In this simple experiment, leaf discs are cut from a plant and placed in a solution containing bicarbonate ions. The rate at which the leaf discs rise to the surface of the solution, releasing oxygen bubbles, is used to estimate the rate of photosynthesis.
Carbon Isotope Techniques:
- Carbon isotope labeling involves introducing a radioactive or stable isotope of carbon (usually carbon-14 or carbon-13) into the plant's carbon dioxide supply. Researchers can then track the movement of these isotopes through the photosynthetic process, providing insights into carbon fixation and flow.
Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) Fluorometry:
- PAM fluorometers are specialized devices that measure the efficiency of photosystem II (PSII), a key component of the photosynthetic machinery. These instruments provide detailed information about the performance of PSII under varying conditions.
Remote Sensing:
- Remote sensing techniques, such as satellite or drone-based imaging, can provide valuable data on the photosynthetic activity of large agricultural or natural ecosystems. These methods use sensors to detect changes in vegetation color, which can be correlated with photosynthesis.
Chamber Systems:
- Enclosed chamber systems are used to measure photosynthesis in controlled environments. Plants are placed in chambers, and environmental conditions, such as light and CO2 concentration, can be manipulated to study their effects on photosynthesis.
Stable Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (IRMS):
- IRMS is used to analyze the stable isotopic composition of plant tissues. This technique can help researchers trace the origin of carbon atoms in plant compounds and understand carbon cycling in ecosystems.
Electrochromic Leaf Stickers:
- These stickers change color in response to changes in leaf water content, which is influenced by photosynthesis. They can provide real-time information about a plant's photosynthetic activity.
The choice of method depends on the specific research questions and the level of detail required. Different techniques offer insights into different aspects of photosynthesis, from basic rates of gas exchange to the molecular processes occurring within plant cells.