What slows down the rate of photosynthesis?
Several factors can slow down the rate of photosynthesis in plants. Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing plant growth and addressing environmental challenges. Here are some key factors that can reduce the rate of photosynthesis:
1. Insufficient Light:
- Limited light availability, such as during cloudy days or in shaded areas, can slow down photosynthesis. Light is one of the primary energy sources for photosynthesis, so reduced light levels lead to lower rates of photosynthesis.
2. Low Temperature:
- Photosynthesis is temperature-sensitive. While moderate temperatures promote photosynthesis, extremely low temperatures can significantly slow down the process. Cold temperatures can affect enzyme activity and the fluidity of cell membranes, both of which are essential for photosynthesis.
3. Inadequate Carbon Dioxide (CO2):
- Insufficient levels of carbon dioxide can limit the rate of photosynthesis. When CO2 concentrations are low, the plant cannot efficiently carry out the carbon fixation process, reducing its photosynthetic capacity.
4. Water Stress:
- Water scarcity or drought conditions can slow down photosynthesis. Water is essential for the transport of minerals, including those used in photosynthesis, as well as for maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells. When water is limited, stomata may close to reduce water loss through transpiration, limiting CO2 intake and photosynthesis.
5. High Light Intensity:
- While low light intensity can limit photosynthesis, extremely high light intensity can also slow it down. Excess light can damage the photosynthetic apparatus, including chlorophyll molecules and photosystems, through a process called photoinhibition.
6. Nutrient Deficiency:
- A lack of essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, can impair photosynthesis. These nutrients are vital for the production of chlorophyll and enzymes involved in photosynthesis.
7. Air Pollution:
- Air pollutants like ozone (O3) can damage plant tissues and interfere with photosynthesis. Ozone can disrupt chloroplast function and reduce photosynthetic rates.
8. Pathogens and Pests:
- Plant diseases, as well as herbivorous pests, can damage plant tissues and reduce the overall surface area available for photosynthesis. This can lead to a decrease in photosynthetic rates.
9. Environmental Stressors:
- Stressors such as excess salinity, heavy metals, or pollutants in the soil can negatively affect plant health and photosynthesis. These stressors can disrupt cellular processes and inhibit photosynthesis.
10. Genetic Factors:- The genetic makeup of a plant can influence its photosynthetic efficiency. Some plant varieties may be better adapted to low-light or stressful environments, while others may have genetic traits that promote higher photosynthetic rates.
11. Seasonal Changes:- Seasonal variations, including changes in day length and temperature, can impact photosynthesis. For example, during the winter months, reduced daylight hours and colder temperatures can slow down photosynthesis in many plants.
It's important to note that these factors can interact with each other, leading to complex effects on photosynthesis. Additionally, different plant species have varying tolerances and responses to these factors. Understanding these limitations and stressors is essential for agriculture, forestry, and conservation efforts to optimize plant growth and resilience in changing environments.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis Rate: An Overview
The rate of photosynthesis is the speed at which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and glucose. It is affected by a variety of factors, both internal and external.
Internal factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis include:
- Chlorophyll concentration: Chlorophyll is the green pigment in plants that absorbs sunlight energy. The more chlorophyll a plant has, the faster it can photosynthesize.
- Enzyme activity: Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions. Photosynthesis requires a number of different enzymes, and their activity can be affected by factors such as temperature and pH.
External factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis include:
- Light intensity: Plants need light to photosynthesize. The brighter the light, the faster the rate of photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials used in photosynthesis. The higher the carbon dioxide concentration, the faster the rate of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: Plants need a certain temperature range to photosynthesize. The optimal temperature for photosynthesis varies depending on the plant species.
- Water availability: Water is another raw material used in photosynthesis. If plants do not have enough water, the rate of photosynthesis will slow down.
- Nutrient availability: Plants need nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus to photosynthesize. If plants do not have enough nutrients, the rate of photosynthesis will slow down.
Other environmental factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis include wind speed, humidity, air pollution, and salinity.
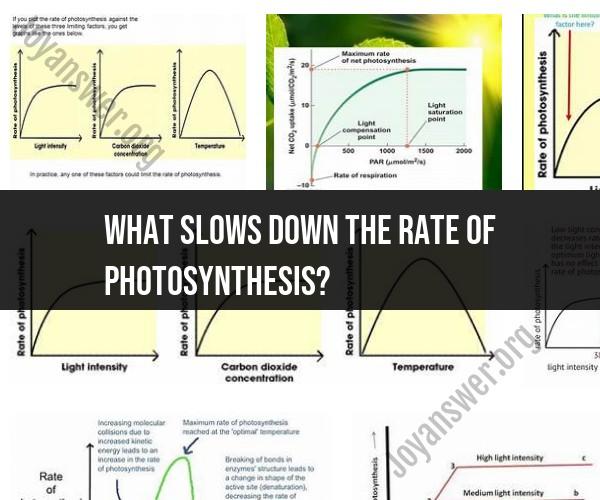
Understanding the Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
A limiting factor is a factor that prevents a process from proceeding at its maximum rate. In photosynthesis, the limiting factor is the factor that is in shortest supply. For example, if a plant has plenty of water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients, but not enough light, then light will be the limiting factor.
If you want to increase the rate of photosynthesis, you need to focus on increasing the supply of the limiting factor. For example, if light is the limiting factor, you can increase the rate of photosynthesis by providing the plant with more light.
Environmental Factors and Photosynthesis Rate
Environmental factors can have a significant impact on the rate of photosynthesis. For example, plants that grow in full sun will typically have a higher rate of photosynthesis than plants that grow in shade. This is because plants in full sun have access to more light, which is the limiting factor for photosynthesis.
Other environmental factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis include temperature, carbon dioxide concentration, water availability, and nutrient availability.
Farmers and greenhouse operators can manipulate environmental factors to optimize the rate of photosynthesis and increase crop yields. For example, farmers can plant crops in full sun, fertilize crops to increase nutrient availability, and irrigate crops to ensure adequate water availability. Greenhouse operators can control the temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide concentration to optimize the rate of photosynthesis.
By understanding the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis, you can take steps to increase the rate of photosynthesis and improve plant growth.