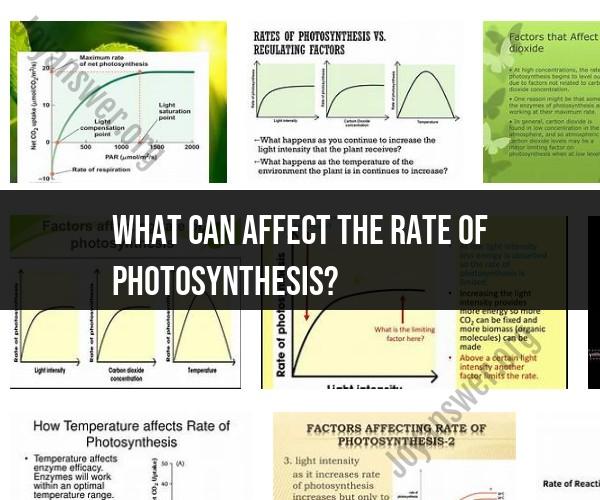
What can affect the rate of photosynthesis?
The rate of photosynthesis, the process by which green plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy (usually in the form of glucose), can be influenced by a variety of environmental and biological factors. Here are some key factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis:
1. Light Intensity:
- Light is one of the most critical factors affecting photosynthesis. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis generally increases until it reaches a point of saturation, beyond which further increases in light intensity have no additional effect.
2. Light Spectrum:
- Different pigments in chloroplasts absorb light of specific wavelengths. Chlorophyll, for example, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red parts of the spectrum. Variations in the type and quality of light can affect photosynthesis rates.
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Concentration:
- Adequate carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis. An increase in CO2 concentration can lead to an increase in photosynthetic rate, up to a certain point where it becomes a limiting factor.
4. Temperature:
- Photosynthesis is temperature-sensitive. As temperature increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis, up to an optimal temperature. Beyond this point, high temperatures can denature enzymes involved in the process, leading to a decrease in photosynthesis.
5. Water Availability:
- Water is a critical component of photosynthesis, as it is used in the light-dependent reactions. Drought or water scarcity can limit photosynthesis.
6. Nutrient Availability:
- Essential nutrients, particularly minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are necessary for plant growth and photosynthesis. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can limit photosynthesis.
7. Chlorophyll Content:
- The amount of chlorophyll in plant cells can affect photosynthesis. More chlorophyll generally leads to higher photosynthetic rates.
8. Leaf Structure and Surface Area:
- The structure and surface area of leaves play a role in photosynthesis. Leaves with a larger surface area and more chloroplasts are typically more efficient at photosynthesis.
9. Environmental Stressors:
- Factors such as pollution, excess salinity, and high levels of ozone can negatively impact photosynthesis by damaging plant cells and interfering with metabolic processes.
10. Biological Factors:- The type of plant, its age, and its genetic makeup can influence photosynthetic rates. Some plants are adapted to low-light conditions and may have specialized mechanisms for efficient photosynthesis in those environments.
11. Photoperiod:- The length of the day (photoperiod) can influence photosynthesis in some plants. Certain plants, like long-day or short-day plants, have specific photoperiod requirements for optimal photosynthesis.
12. Herbivory and Pathogens:- Damage caused by herbivores or pathogens can reduce the leaf surface area available for photosynthesis and disrupt cellular processes, affecting the rate of photosynthesis.
Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing photosynthesis in agricultural and ecological contexts and for studying the responses of plants to changing environmental conditions. Researchers and plant scientists often study these factors to improve crop yields and address ecological challenges.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. The rate of photosynthesis can be affected by a number of environmental factors, including:
- Light intensity: Plants need light to photosynthesize. The brighter the light, the faster the rate of photosynthesis.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Carbon dioxide is one of the raw materials used in photosynthesis. The higher the carbon dioxide concentration, the faster the rate of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: Plants need a certain temperature range to photosynthesize. The optimal temperature for photosynthesis varies depending on the plant species.
- Water availability: Water is another raw material used in photosynthesis. If plants do not have enough water, the rate of photosynthesis will slow down.
- Nutrient availability: Plants need nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus to photosynthesize. If plants do not have enough nutrients, the rate of photosynthesis will slow down.
Other environmental factors that can affect the rate of photosynthesis include:
- Wind speed: High wind speeds can damage leaves and reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
- Humidity: Low humidity can cause plants to lose water, which can slow down photosynthesis.
- Air pollution: Air pollution can block sunlight and reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
- Salinity: High salinity in the soil or water can reduce the rate of photosynthesis.
Controlling Photosynthesis Rate
The rate of photosynthesis can be controlled by manipulating the environmental factors that affect it. For example, farmers can increase crop yields by increasing the light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and nutrient availability. Greenhouse operators can also control the temperature and humidity to optimize photosynthesis.
Key Variables and Considerations
When controlling the rate of photosynthesis, it is important to consider the following variables:
- The type of plant: Different plants have different optimal conditions for photosynthesis. For example, some plants prefer bright light, while others prefer shade.
- The stage of plant growth: The rate of photosynthesis varies depending on the stage of plant growth. For example, young plants typically have a lower rate of photosynthesis than mature plants.
- The availability of resources: It is important to make sure that plants have access to all of the resources they need to photosynthesize, including light, carbon dioxide, water, and nutrients.
By understanding the factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis, farmers and greenhouse operators can control photosynthesis to optimize crop yields.