What does gross profit margin mean?
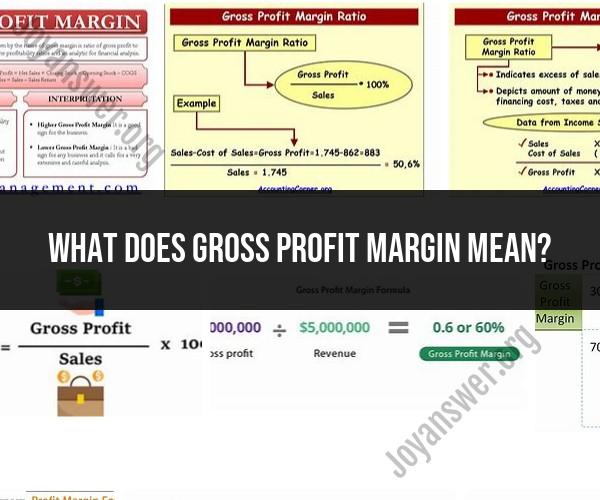
The gross profit margin is a financial metric that measures a company's profitability by assessing the relationship between its gross profit and its total revenue or sales. It is expressed as a percentage and provides insights into how effectively a company is managing its production or service costs in relation to its revenue. The formula to calculate the gross profit margin is:
Gross Profit Margin (%) = (Gross Profit / Total Revenue) x 100
Where:
Gross Profit is the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). In other words, it's the profit a company makes after deducting the direct costs associated with producing or delivering its products or services.
Total Revenue is the total income generated from the sale of products or services before deducting any expenses.
The gross profit margin serves several important purposes:
Profitability Assessment: It helps assess the efficiency of a company's core operations in generating profits. A higher gross profit margin generally indicates better profitability, as it suggests the company is effectively managing its production costs.
Comparison: Businesses can use gross profit margins to compare their financial performance over time or against competitors in the same industry. A higher margin may indicate a competitive advantage in cost management.
Investor and Lender Confidence: Investors and lenders often use gross profit margin as a key indicator of a company's financial health and management effectiveness. A healthy margin can inspire confidence in stakeholders.
Strategic Decision-Making: Companies can use gross profit margin data to make strategic decisions. For example, if the margin is declining, management may explore ways to reduce production costs or adjust pricing strategies.
Industry Benchmark: The gross profit margin can serve as a benchmark for what is considered a healthy margin within a specific industry. It helps companies understand where they stand relative to industry standards.
It's important to note that while a higher gross profit margin is generally seen as positive, the interpretation of the margin can vary by industry. Some industries naturally have higher production costs, leading to lower margins. Therefore, it's crucial to consider industry norms when evaluating a company's gross profit margin. Additionally, the gross profit margin is just one of many financial metrics used to assess a company's overall financial performance and should be analyzed alongside other key indicators for a comprehensive understanding of the business's health.