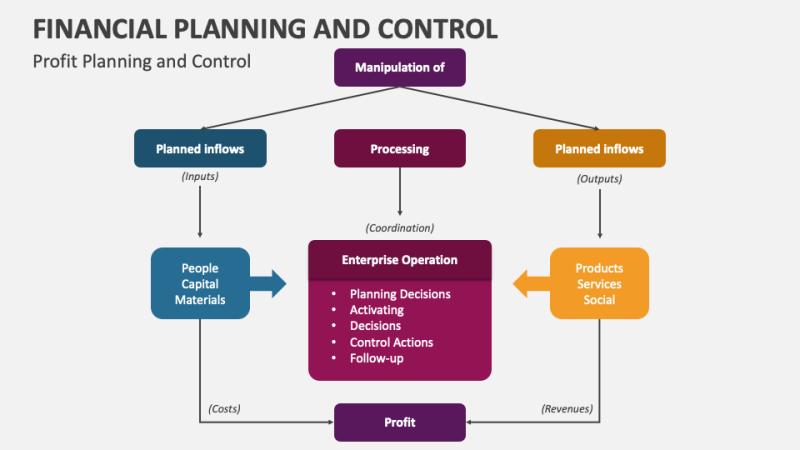
What is strategic financial planning?
Strategic financial planning is the process of aligning an organization’s long-term financial goals with its broader mission, vision, and strategic objectives. It’s not just about budgeting for the next quarter — it’s about creating a roadmap that ensures financial decisions support sustainable growth, competitive advantage, and resilience over time.
Key Concepts in Strategic Financial Planning
1. Long-Term Vision Alignment
Strategic financial planning ensures that financial resources are directed toward the organization’s big-picture goals. For example, a tech company might plan funding for R&D to stay ahead of innovation trends over the next 5–10 years.
2. Comprehensive Financial Forecasting
It involves projecting revenues, expenses, cash flows, and capital needs over multiple years. These forecasts help anticipate funding requirements, potential shortfalls, and investment opportunities.
3. Risk Assessment and Management
Strategic planning evaluates potential risks — such as market volatility, regulatory changes, or supply chain disruptions — and builds financial buffers or contingency strategies to manage them.
4. Capital Allocation
Determining how to allocate resources among various initiatives (e.g., expansion, technology upgrades, marketing) to maximize returns and support strategic priorities.
5. Performance Metrics and KPIs
Setting measurable targets like return on investment (ROI), profit margins, or debt-to-equity ratios to monitor progress and adjust strategies as needed.
6. Integration with Business Strategy
Strategic financial planning isn’t an isolated finance function — it works hand-in-hand with marketing, operations, and HR strategies to ensure every department moves toward the same objectives.
7. Continuous Review and Adaptation
Because markets and business conditions change, strategic financial plans are reviewed regularly, allowing organizations to pivot when needed.
In short:
Strategic financial planning is about proactively managing an organization’s finances to ensure long-term stability, growth, and alignment with overall business goals — rather than reacting to short-term financial pressures.
What Is Strategic Financial Planning?
Strategic financial planning is the process of defining a company's long-term financial goals and creating a detailed roadmap to achieve them.
How Do Companies Create a Strategic Financial Plan?
Creating a strategic financial plan is a systematic process that requires a comprehensive understanding of both internal and external factors.
Assess Current Financial Health: The first step is to thoroughly evaluate the company's current financial position.
This includes analyzing financial statements such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to understand profitability, liquidity, and solvency. Establish Clear Financial Goals: Based on the assessment, companies set clear, measurable, and realistic long-term financial objectives.
These goals could include increasing revenue by a certain percentage, improving profit margins, entering new markets, or acquiring new assets. Analyze and Forecast: The company conducts a market analysis to understand industry trends, competitor actions, and economic conditions.
It then creates financial forecasts, projecting future revenues, expenses, and cash flow under different scenarios to prepare for various outcomes. Formulate Strategic Initiatives: This step involves developing specific initiatives and strategies to achieve the established goals.
This could include new pricing strategies, cost management plans, or decisions on where to invest capital. Allocate Resources and Implement: The plan outlines how to wisely allocate financial, human, and technological resources to support the strategic initiatives.
The implementation phase requires clear communication and accountability across the organization. Monitor and Adjust: A strategic plan is a living document.
Companies must continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) against their plan's benchmarks and be ready to adapt their strategy as market conditions or internal performance change.
What Are the Key Elements of Strategic Planning in Finance?
A robust strategic financial plan integrates several critical components:
Long-Term Goals: Defining the company's overarching financial vision, often for a period of 3-5 years.
Financial Forecasting: Projecting future financial performance to anticipate opportunities and challenges.
Capital Budgeting: A detailed plan for major investments in long-term assets like equipment, technology, or facilities.
Risk Management: Identifying and planning for potential financial risks, such as market volatility, credit risk, or operational disruptions.
Budgeting: Creating a detailed plan for expected revenues and expenses, ensuring that resource allocation is aligned with strategic goals.
Performance Metrics: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and evaluate the plan's effectiveness.
Financing Strategy: A plan for how to fund the company's growth, whether through internal funds, debt financing, or equity.
How Can Financial Planning Improve Business Resilience?
Strategic financial planning is a crucial tool for building a resilient business—one that can withstand economic downturns and unexpected crises.
Proactive Risk Mitigation: By identifying and planning for potential risks in advance, a company can develop contingency plans, build emergency reserves, and create a more diversified revenue stream, making it less vulnerable to single points of failure.
Optimized Cash Flow Management: A solid financial plan helps a company maintain a healthy cash flow, ensuring it has the liquidity to meet its obligations and continue operations even during periods of reduced revenue.
Informed Decision-Making: When faced with a crisis, a strategic financial plan provides a framework for making fast, data-driven decisions.
It helps leadership understand which expenses can be cut, which investments should be protected, and how to preserve core business functions. Foundation for Agility: While strategic planning is long-term, it provides the foundational knowledge needed for short-term agility. By having a clear understanding of its financial position and goals, a company can quickly pivot to capitalize on new opportunities or respond to threats.
5. What’s the Difference Between Strategic and Operational Planning?
While both are essential for business success, strategic and operational planning serve different purposes and operate on different time scales.
Time Frame: Strategic planning is long-term, typically spanning 3-5 years or more.
It sets the company's ultimate direction and vision. Operational planning is short-term, usually covering a period of one year or less. It focuses on the day-to-day activities required to achieve the strategic goals. Scope: Strategic planning is broad and company-wide, addressing the overarching mission and market position.
Operational planning is narrower, focusing on specific departments, processes, and tasks. Purpose: Strategic planning is about what the company wants to achieve and why.
It defines the destination. Operational planning is about how the company will get there, detailing the specific actions, resources, and timelines. Level of Detail: A strategic plan is high-level, with broad objectives and key initiatives.
An operational plan is highly detailed, outlining specific tasks, responsibilities, and performance metrics for employees.