What is the formula for calculating the current ratio?
The current ratio is a financial metric used to evaluate a company's short-term liquidity and its ability to cover its short-term liabilities with its short-term assets. The formula for calculating the current ratio is as follows:
Here's a breakdown of the components:
Current Assets:
- Current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used up within one year. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments.
Current Liabilities:
- Current liabilities are obligations that are due within one year. This includes accounts payable, short-term debt, and other current liabilities.
The current ratio provides insight into a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations. A ratio above 1 indicates that the company has more current assets than current liabilities, suggesting that it can cover its short-term obligations. However, a very high current ratio may suggest inefficiency in managing assets. On the other hand, a ratio below 1 indicates potential difficulty in covering short-term obligations.
While the current ratio is a useful measure of short-term liquidity, it's important to interpret it in the context of the industry and company-specific circumstances. Comparing the current ratio to industry benchmarks or historical ratios for the same company can provide additional insights into its financial health.
The current ratio is a fundamental financial metric that provides valuable insights into a company's short-term liquidity and financial health. It helps assess a company's ability to meet its immediate obligations, such as paying bills and covering operational costs, using its current assets.
Unveiling the Current Ratio Formula:
The current ratio formula is a simple yet powerful tool for financial analysis:
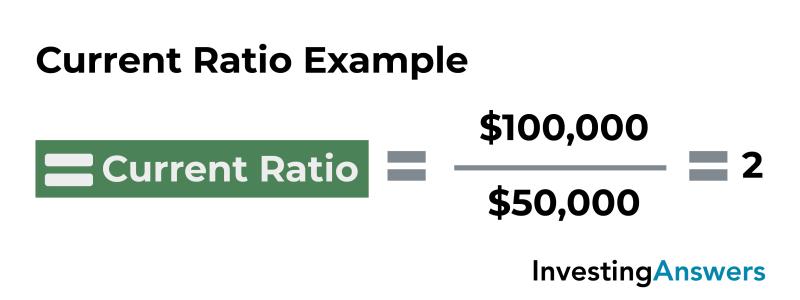
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
This formula measures a company's ability to cover its current liabilities with its current assets. A higher current ratio indicates a stronger financial position, while a lower ratio suggests potential liquidity concerns.
Breaking Down the Formula:
Current Assets: These are resources that can be readily converted into cash within one year. Examples include cash, accounts receivable (money owed by customers), inventory, and prepaid expenses.
Current Liabilities: These are obligations that must be paid within the next 12 months. Examples include accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), short-term loans, accrued expenses (wages or rent owed but not yet paid), and the current portion of long-term debt.
Identifying Current Assets:
Current assets are typically listed on a company's balance sheet under the heading "Current Assets." These assets represent the company's resources that can be easily turned into cash to pay off short-term obligations.
Understanding Current Liabilities:
Current liabilities are also found on the balance sheet under the heading "Current Liabilities." These obligations represent the company's short-term debts that must be paid within the next year.
Applying the Formula to Real-World Scenarios:
To calculate the current ratio for a company, divide the total current assets by the total current liabilities. For instance, consider a company with the following financial information:
Current Assets: $1,000,000
Current Liabilities: $500,000
In this scenario, the current ratio would be:
Current Ratio = $1,000,000 / $500,000 = 2:1
This indicates that the company has $2 of current assets for every $1 of current liabilities, suggesting a strong liquidity position.
The current ratio is a valuable tool for financial analysts, investors, and creditors to assess a company's short-term financial health and ability to meet its obligations. A healthy current ratio provides confidence in a company's ability to manage its short-term finances and navigate through economic cycles.