What is the relationship between circumference and diameter?
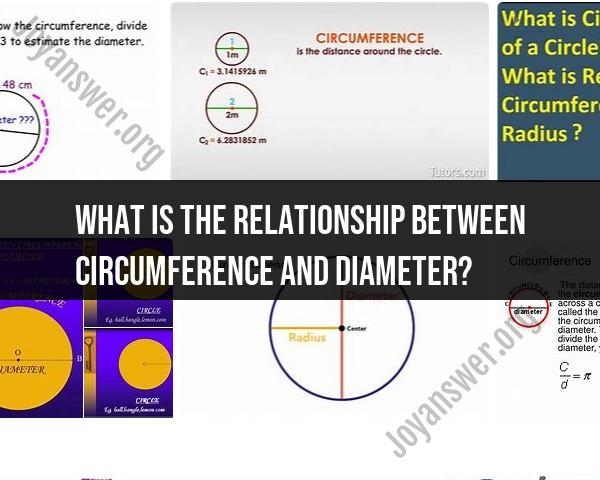
The relationship between the circumference and diameter of a circle is a fundamental and well-defined mathematical concept. It is described by the mathematical constant π (pi), which is approximately equal to 3.14159. The relationship can be expressed as follows:
Circumference (C) is directly proportional to the Diameter (D) of a circle, and this relationship can be given by the formula:
In this equation:
- C represents the circumference of the circle.
- D represents the diameter of the circle.
- π (pi) is a constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
This means that if you know the diameter of a circle, you can find its circumference by multiplying the diameter by π, and conversely, if you know the circumference, you can find the diameter by dividing the circumference by π.
Additionally, you can also find the radius of a circle (the distance from the center to the edge) from the diameter or vice versa:
- Radius (R) is half of the diameter, so .
- The relationship between the circumference and the radius can be expressed as .
Understanding this relationship is essential in various mathematical and scientific contexts, especially when working with circles and circular objects in geometry, trigonometry, and physics.
Exploring the Relationship Between Circumference and Diameter
The circumference of a circle is the total distance around its outer edge, while the diameter is the length of a straight line passing through the center of the circle and connecting two points on its circumference. These two measures are closely related, and their relationship is expressed by the constant π (pi).
2. The Constant π (Pi) and Its Role in Circumference Calculation
Pi (π) is a mathematical constant that represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. It is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite decimal expansion. The value of π is approximately 3.14159.
The formula for calculating the circumference (C) of a circle given its diameter (d) is:
C = πd
This formula highlights the direct relationship between circumference and diameter, with π serving as the proportionality constant.
Circumference-Diameter Relationship in Geometry
The circumference-diameter relationship is fundamental in geometry and has numerous applications. For instance, it allows us to calculate the circumference of a circle if we know its diameter, and vice versa. It also plays a crucial role in understanding other geometric concepts related to circles, such as arc length, sector area, and angular relationships.
Real-World Applications of Circumference and Diameter
The concepts of circumference and diameter have numerous real-world applications, including:
Measuring circular objects: From determining the distance a wheel travels in one revolution to calculating the amount of material needed for a circular pipe, circumference and diameter are essential for measuring and designing circular objects.
Navigation and mapping: Circumference and diameter are used in navigation and mapping to determine distances and plot routes. For instance, the circumference of the Earth is used to calculate distances between locations along a curved surface.
Engineering and design: In engineering and design, circumference and diameter are crucial for designing circular components, such as gears, bearings, and turbines. They also play a role in architectural design, landscaping, and interior layouts.
Fun and Educational Activities Involving Circles and Pi
Here are some fun and educational activities to explore circles and pi:
Measuring circular objects: Gather various circular objects, such as coins, plates, or lids, and measure their circumference and diameter using a ruler or tape measure. Calculate the ratio of circumference to diameter for each object and observe how it approximates the value of pi.
Creating circle art: Use a compass and ruler to draw various circles of different sizes. Experiment with dividing the circles into equal sections and shading them to create interesting patterns. Explore the relationship between the number of sections and the angle each section represents.
Estimating pi using everyday items: Gather cylindrical objects like cans or bottles and measure their circumference and diameter. Calculate the ratio of circumference to diameter for each object and compare the average value to the actual value of pi.
Exploring pi in nature: Research examples of circular patterns in nature, such as sunflower arrangements, ripples in water, or the arrangement of seeds in a fruit. Discuss how these patterns relate to the concept of pi and its significance in natural phenomena.