What is the difference between cellular respiration and breathing?
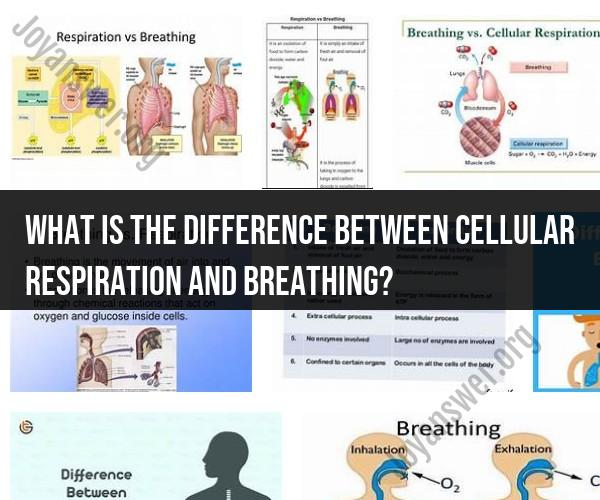
Cellular respiration and breathing are two distinct processes related to obtaining energy and oxygen in living organisms. Here are the key differences between cellular respiration and breathing:
1. Process and Location:
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that occurs within cells, specifically in the mitochondria. It is the process by which cells extract energy from glucose (and other organic molecules) in the presence of oxygen. Cellular respiration involves a series of chemical reactions, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Breathing: Breathing, also known as respiration or ventilation, is a physical process that occurs at the organism level. It involves the inhalation of oxygen-rich air and the exhalation of carbon dioxide-rich air. Breathing takes place in the respiratory system, primarily in the lungs.
2. Function:
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration is the process by which cells produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells. It converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.
Breathing: Breathing is the process of exchanging gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the external environment. It provides the oxygen necessary for cellular respiration and removes the waste product, carbon dioxide.
3. Biological Level:
Cellular Respiration: It occurs at the cellular level and is a fundamental process in all living cells, from single-celled organisms like bacteria to complex multicellular organisms like humans.
Breathing: It occurs at the organismal level and is primarily associated with animals with respiratory systems, such as mammals, birds, and reptiles. Plants and some single-celled organisms do not "breathe" in the same way animals do.
4. Energy Production:
Cellular Respiration: The primary purpose of cellular respiration is to produce ATP, which is used by cells for various energy-requiring processes, including muscle contraction, active transport, and synthesis of macromolecules.
Breathing: Breathing itself does not produce energy. Instead, it provides the oxygen needed for cellular respiration, where the actual energy production occurs.
5. Waste Products:
Cellular Respiration: The waste products of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water. These waste products are expelled from cells and transported to the lungs and kidneys for removal from the body.
Breathing: The process of breathing helps remove excess carbon dioxide (a waste product of cellular respiration) from the body by exhaling it into the atmosphere.
In summary, cellular respiration is a metabolic process that occurs within cells and is responsible for producing ATP by breaking down glucose with oxygen. Breathing, on the other hand, is the physical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide at the organismal level. Breathing facilitates the exchange of gases between the body and the environment and provides the oxygen necessary for cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration vs. Breathing: Key Differences Explained
Cellular respiration and breathing are two related but distinct biological processes.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other nutrients to produce energy in the form of ATP. This process takes place inside cells in the mitochondria.
Breathing, also known as ventilation, is the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the body. This process takes place in the lungs.
Key differences between cellular respiration and breathing:
| Characteristic | Cellular respiration | Breathing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process by which cells break down glucose and other nutrients to produce energy | The process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the body |
| Location | Inside cells in the mitochondria | In the lungs |
| Purpose | To produce energy | To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide |
| Involved gases | Oxygen and glucose | Oxygen and carbon dioxide |
| End products | ATP, carbon dioxide, and water | Carbon dioxide |
Relationship between cellular respiration and breathing
Breathing provides the oxygen needed for cellular respiration. The oxygen that is inhaled enters the bloodstream and is carried to the cells. Inside the cells, the oxygen is used to break down glucose and other nutrients to produce energy.
The carbon dioxide that is produced during cellular respiration is released into the bloodstream and is carried to the lungs. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled from the body.
Conclusion
Cellular respiration and breathing are two essential biological processes that work together to provide the body with energy and to remove waste products. By understanding the key differences between these two processes, we can better appreciate their importance to life.