What is cellular respiration and how does it occur?
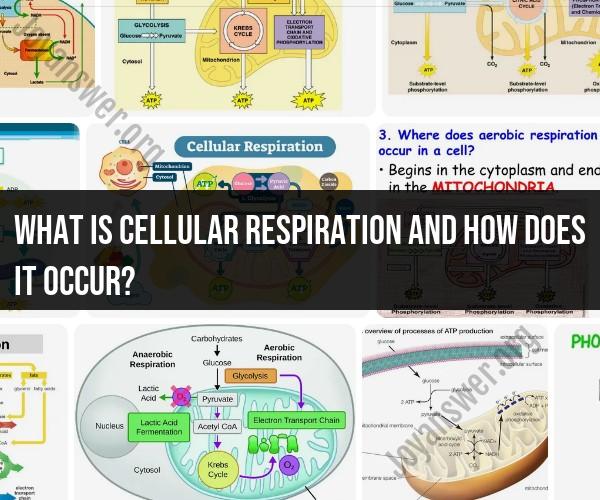
Cellular respiration is a vital metabolic process that occurs within cells to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It is the process by which cells extract energy from organic molecules, such as glucose, and convert it into a usable form of chemical energy. Cellular respiration typically takes place in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. The process of cellular respiration can be summarized in three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the electron transport chain.
Here is an overview of how cellular respiration occurs:
1. Glycolysis:
Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
During glycolysis, a molecule of glucose (a six-carbon sugar) is split into two molecules of pyruvate (a three-carbon compound). This process does not require oxygen and is anaerobic.
As glucose is broken down, energy is released, and some ATP molecules are generated directly. NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is also produced as an electron carrier.
2. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle):
If oxygen is available, pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria, where the citric acid cycle takes place.
In the citric acid cycle, each pyruvate molecule is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and generating more ATP, NADH, and another electron carrier called FADH2 (flavin adenine dinucleotide).
3. Electron Transport Chain (ETC):
The electron transport chain is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
NADH and FADH2 molecules, which were produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, donate electrons to the electron transport chain.
As electrons move through the chain, they release energy that is used to pump protons (hydrogen ions) across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space, creating an electrochemical gradient.
The flow of protons back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase enzyme complexes drives the synthesis of ATP from adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) in a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
Oxygen serves as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, combining with electrons and protons to form water. This step is essential for the continued functioning of the chain.
4. ATP Production:
The energy generated during glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain is used to produce a large amount of ATP.
The total ATP yield from one molecule of glucose through cellular respiration can vary but is typically around 36-38 ATP molecules. This energy is readily available for the cell to carry out various functions and processes.
In summary, cellular respiration is a multi-stage process that breaks down glucose and other organic molecules to produce ATP, the cell's primary energy currency. Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain are the key stages involved in this process. Cellular respiration is essential for the survival and functioning of all aerobic organisms, as it provides the energy required for cellular activities and processes.
Cellular Respiration: Process and Mechanisms Explained
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells convert chemical energy from food into cellular energy in the form of ATP. It takes place in all living cells and is essential for life.
Cellular respiration is a complex process that can be divided into four main stages:
- Glycolysis: Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. It breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing two molecules of ATP in the process.
- Pyruvate oxidation: Pyruvate oxidation takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and requires oxygen. It converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, releasing carbon dioxide and producing one molecule of NADH in the process.
- Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle): The TCA cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and requires oxygen. It breaks down acetyl-CoA into carbon dioxide and water, producing two molecules of ATP, six molecules of NADH, and two molecules of FADH2 in the process.
- Oxidative phosphorylation: Oxidative phosphorylation takes place on the inner mitochondrial membrane and requires oxygen. It uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP.
The overall chemical equation for cellular respiration is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + 38 ATP
This equation shows that one molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen produce six molecules of carbon dioxide, six molecules of water, and 38 molecules of ATP.
Mechanisms of cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is mediated by a variety of enzymes and other proteins. These enzymes and proteins catalyze the different reactions of cellular respiration and ensure that the process runs efficiently.
One of the key mechanisms of cellular respiration is the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. This process releases energy, which is used to produce ATP.
Conclusion
Cellular respiration is a complex but essential process that provides cells with the energy they need to survive. It is mediated by a variety of enzymes and other proteins, which work together to ensure that the process runs efficiently.
The Intricacies of Cellular Respiration: A Comprehensive Overview
Cellular respiration is a complex biochemical process that occurs in all living cells. It is the process by which cells convert chemical energy from food into cellular energy in the form of ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is used to power all cellular activities.
Cellular respiration can be divided into four main stages: glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. It does not require oxygen and breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing two molecules of ATP in the process.
Pyruvate oxidation takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and requires oxygen. It converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, releasing carbon dioxide and producing one molecule of NADH in the process.
The citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and also requires oxygen. It breaks down acetyl-CoA into carbon dioxide and water, producing two molecules of ATP, six molecules of NADH, and two molecules of FADH2 in the process.
Oxidative phosphorylation takes place on the inner mitochondrial membrane and is the final stage of cellular respiration. It uses the energy from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP.
Cellular respiration is a highly regulated process and is controlled by a variety of factors, including the availability of oxygen and nutrients, the energy needs of the cell, and the levels of ATP and other metabolites.
Intricacies of cellular respiration
One of the most intricate aspects of cellular respiration is the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen. This process releases energy, which is used to produce ATP.
The electron transport chain is a very efficient process and can produce up to 34 molecules of ATP per molecule of NADH and 12 molecules of ATP per molecule of FADH2.
Another intricate aspect of cellular respiration is the regulation of the process. Cellular respiration is regulated by a variety of factors, including the availability of oxygen and nutrients, the energy needs of the cell, and the levels of ATP and other metabolites.
This regulation ensures that cellular respiration runs efficiently and that the cell produces the amount of ATP it needs.
How Cellular Respiration Occurs: Insights into the Process
Cellular respiration is a process that is essential for life. It is the process by which cells convert chemical energy from food into cellular energy in the form of ATP