How do you find linear acceleration?
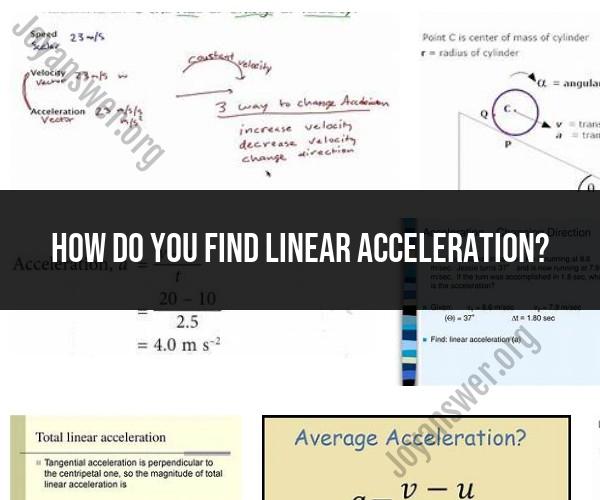
Linear acceleration is a measure of how quickly an object's velocity (speed and direction) changes over time. You can calculate linear acceleration using the following formula:
Linear Acceleration (a) = Change in Velocity (Δv) / Time Interval (Δt)
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to find linear acceleration:
Determine Initial and Final Velocities: To calculate linear acceleration, you need to know the initial velocity (starting speed and direction) and the final velocity (ending speed and direction) of the object. Make sure the velocities are in the same units (e.g., meters per second, miles per hour).
Calculate Change in Velocity: Subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity to find the change in velocity (Δv). The formula is:
Δv = Final Velocity - Initial Velocity
Ensure that the direction of velocity change is taken into account. If the object is slowing down, the change in velocity will be negative.
Determine the Time Interval: Determine the time interval (Δt) over which the velocity change occurs. This is typically given in seconds.
Apply the Formula: Use the formula for linear acceleration:
a = Δv / Δt
Plug in the values you found for Δv and Δt in the appropriate units.
Calculate Linear Acceleration: Perform the division to calculate the linear acceleration. The unit of linear acceleration will be the unit of velocity (e.g., meters per second) divided by the unit of time (e.g., seconds), resulting in units such as meters per second squared (m/s²) or miles per hour per second (mph/s).
Here's an example:
Suppose a car starts from rest (initial velocity = 0 m/s) and accelerates to a final velocity of 30 m/s in 5 seconds.
- Initial Velocity (u) = 0 m/s
- Final Velocity (v) = 30 m/s
- Time Interval (Δt) = 5 seconds
Now, calculate Δv:
Δv = v - uΔv = 30 m/s - 0 m/sΔv = 30 m/s
Next, calculate linear acceleration (a):
a = Δv / Δta = 30 m/s / 5 sa = 6 m/s²
So, the linear acceleration of the car is 6 meters per second squared (6 m/s²) during this acceleration period.
Linear Acceleration: Understanding the Basics of Motion
Linear acceleration is the rate of change of an object's velocity in a straight line. It is a vector quantity, which means that it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of linear acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2). The direction of linear acceleration is the same as the direction of the change in velocity.
Linear acceleration can be caused by a force acting on an object. According to Newton's second law of motion, the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration. This means that the greater the force acting on an object, or the smaller the mass of the object, the greater its acceleration will be.
Linear acceleration is also affected by the friction between the object and the surface it is moving on. Friction is a force that opposes motion, so it will reduce the object's acceleration.
Calculating Linear Acceleration: A Step-by-Step Guide
To calculate linear acceleration, you need to know the object's initial velocity, final velocity, and time interval.
The formula for linear acceleration is:
a = (vf - vi) / t
where:
- a is the acceleration (m/s^2)
- vf is the final velocity (m/s)
- vi is the initial velocity (m/s)
- t is the time interval (s)
For example, if an object starts at rest and accelerates to a velocity of 10 m/s in 5 seconds, its acceleration would be:
a = (10 m/s - 0 m/s) / 5 s
a = 2 m/s^2
This means that the object's velocity is increasing by 2 m/s every second.
Acceleration in a Straight Line: How to Find Linear Acceleration
There are a few different ways to find linear acceleration. One way is to use the formula above. Another way is to use a motion sensor. A motion sensor is a device that can measure the velocity of an object.
To use a motion sensor to find linear acceleration, you need to attach the motion sensor to the object and then measure the object's velocity over time. The motion sensor will give you a graph of the object's velocity. The slope of the graph is equal to the object's acceleration.
If the graph is a straight line, then the object is accelerating at a constant rate. If the graph is a curve, then the object is accelerating at a non-constant rate.
Conclusion
Linear acceleration is an important concept in physics. It is used to describe the motion of objects in a straight line. Linear acceleration can be calculated using the formula above or by using a motion sensor.