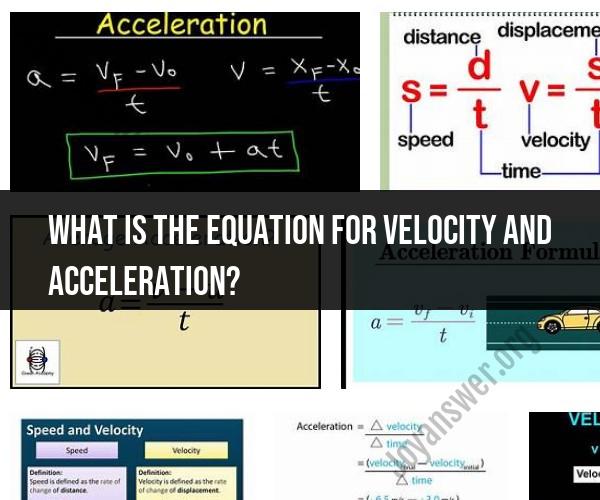
What is the equation for velocity and acceleration?
The equations for velocity and acceleration in physics are fundamental concepts in describing the motion of objects. Here are the equations for velocity and acceleration:
1. Velocity (v):Velocity is a measure of an object's speed and direction of motion. The equation for velocity is:
v = Δx / Δt
- v: Velocity (in meters per second, m/s or any other appropriate units)
- Δx: Displacement or change in position (in meters, m)
- Δt: Change in time (in seconds, s)
In simple terms, velocity is the rate of change of an object's position with respect to time. It tells you how fast an object is moving and in which direction.
2. Acceleration (a):Acceleration measures how quickly an object's velocity changes. The equation for acceleration is:
a = Δv / Δt
- a: Acceleration (in meters per second squared, m/s² or any other appropriate units)
- Δv: Change in velocity (in meters per second, m/s)
- Δt: Change in time (in seconds, s)
Acceleration indicates how much an object's velocity is changing over a specific time interval. If the acceleration is positive, it means the object is speeding up, and if it's negative, it means the object is slowing down.
It's important to note that these equations are simplified versions. In real-world scenarios with varying acceleration, you may need to use calculus to calculate velocity and acceleration as functions of time.
Additionally, there are other equations that relate velocity, acceleration, initial velocity (usually denoted as "u"), final velocity ("v"), time ("t"), and displacement ("s") under different conditions. Some of these equations are derived from the basic equations for velocity and acceleration.
Exploring the Equations for Velocity and Acceleration
Velocity is the rate of change of an object's position. It is a vector quantity, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s). The direction of velocity is the same as the direction of the object's motion.
Acceleration is the rate of change of an object's velocity. It is also a vector quantity. The magnitude of acceleration is measured in meters per second squared (m/s^2). The direction of acceleration is the same as the direction of the change in velocity.
The equations for velocity and acceleration are as follows:
Velocity = (Change in position) / (Time interval)
Acceleration = (Change in velocity) / (Time interval)
These equations can be used to solve a variety of physics problems. For example, you can use them to calculate the velocity of an object, the acceleration of an object, or the time it takes an object to travel a certain distance.
Physics Fundamentals: Understanding Velocity and Acceleration Formulas
Velocity and acceleration are two of the most important concepts in physics. They are used to describe the motion of objects and to predict their future motion.
The velocity of an object can be constant or variable. If the velocity of an object is constant, then the object is moving at a constant speed in a straight line. If the velocity of an object is variable, then the object is accelerating.
The acceleration of an object can be positive or negative. Positive acceleration means that the object is speeding up. Negative acceleration means that the object is slowing down.
The velocity and acceleration of an object are related to each other by the following equation:
Acceleration = (Change in velocity) / (Time interval)
This equation means that the acceleration of an object is equal to the change in its velocity divided by the time interval over which the change occurs.
The Science of Motion: Equations for Speed and Change in Speed
The equations for velocity and acceleration are based on the science of motion. The science of motion is the study of how objects move and why they move the way they do.
The laws of motion were first developed by Isaac Newton in the 17th century. Newton's laws of motion explain how objects move and how they are affected by forces.
The equations for velocity and acceleration are based on Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration.
Conclusion
The equations for velocity and acceleration are two of the most important equations in physics. They are used to describe the motion of objects and to predict their future motion.
The equations for velocity and acceleration are based on the science of motion, which is the study of how objects move and why they move the way they do.
The equations for velocity and acceleration can be used to solve a variety of physics problems, such as calculating the velocity of an object, the acceleration of an object, or the time it takes an object to travel a certain distance.