What are units of angular acceleration?
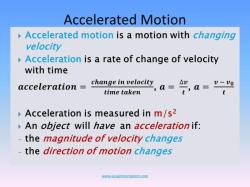
Angular acceleration is a measure of how quickly an object's angular velocity (rate of rotation) changes over time. The units of angular acceleration depend on the system of units you are using. The most common units for angular acceleration are:
Radians per second squared (rad/s²): In the International System of Units (SI), angular acceleration is often measured in radians per second squared. One radian is the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. So, 1 radian per second squared means that the object's angular velocity changes by 1 radian per second every second.
Degrees per second squared (°/s²): In some contexts, especially when degrees are used to measure angles, angular acceleration can be expressed in degrees per second squared. One degree is 1/360th of a full circle.
Revolutions per second squared (rev/s²): In cases where revolutions (or full circles) are used to measure angles, angular acceleration can be given in revolutions per second squared. One revolution is equivalent to 360 degrees.
It's important to use consistent units in calculations involving angular acceleration to ensure accurate and meaningful results. The choice of units depends on the specific context and the conventions used in the problem or within a particular field of science or engineering.
Exploring Units of Angular Acceleration in Physics
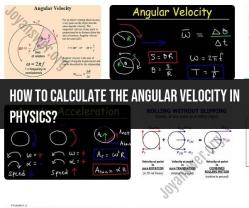
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity. Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement. Therefore, angular acceleration is the rate of change of the rate of change of angular displacement. Angular acceleration is a vector quantity and is measured in radians per second squared (rad/s^2).
Angular Acceleration Measurement and Notation
Angular acceleration is usually denoted by the Greek letter alpha (α). It can be measured using a variety of methods, including:
- Gyroscopes: Gyroscopes are devices that measure angular velocity. By measuring the change in angular velocity over time, angular acceleration can be calculated.
- Accelerometers: Accelerometers are devices that measure acceleration. By measuring the acceleration of an object rotating around a fixed axis, angular acceleration can be calculated.
- Optical encoders: Optical encoders are devices that measure the position of an object. By measuring the change in position of an object rotating around a fixed axis over time, angular acceleration can be calculated.
Calculating and Converting Angular Acceleration Units
Angular acceleration can be calculated using the following equation:
α = Δω / Δt
where:
- α is angular acceleration
- Δω is the change in angular velocity
- Δt is the change in time
Angular acceleration can be converted to other units using the following conversion factors:
- 1 rad/s^2 = 1 revolution per second squared (rps^2)
- 1 rad/s^2 = 1 degree per second squared (dps^2)
Examples
Here are some examples of how to calculate and convert angular acceleration units:
- A wheel accelerates from a standstill to a speed of 100 revolutions per minute (rpm) in 5 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the wheel?
α = Δω / Δt
α = (100 rpm - 0 rpm) / 5 s
α = 20 rpm/s
- A pendulum with a length of 1 meter swings back and forth with a period of 2 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the pendulum at its midpoint?
α = ω² / L
α = (2π rad / 2 s)² / 1 m
α = 4π² rad/s²
- A motor accelerates a rotating object from a speed of 100 rpm to a speed of 200 rpm in 5 seconds. What is the angular acceleration of the object in rad/s^2?
α = Δω / Δt
α = (200 rpm - 100 rpm) / 5 s
α = 20 rpm/s
α = 20 rpm/s * (2π rad / 1 revolution)
α = 40π rad/s²
Angular acceleration is an important concept in physics and engineering. It is used to design and analyze a variety of systems, including rotating machinery, vehicles, and aircraft. By understanding how to calculate and convert angular acceleration units, you can apply these concepts to solve real-world problems.