What is the formula used for calculate acceleration?
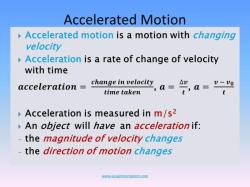
The formula used to calculate acceleration is:
Acceleration (a) = Change in Velocity (Δv) / Change in Time (Δt)
Where:
- Acceleration (a) is measured in meters per second squared (m/s²) or another suitable unit of acceleration.
- Change in Velocity (Δv) is the difference in velocity between two points in time. It is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or another unit of velocity.
- Change in Time (Δt) is the time interval over which the change in velocity occurs. It is measured in seconds (s) or another unit of time.
In simple terms, acceleration is a measure of how quickly an object's velocity is changing. If an object is speeding up, it has positive acceleration. If it is slowing down, it has negative acceleration (also known as deceleration). If its velocity remains constant, the acceleration is zero.
This formula is fundamental in physics and is used to describe the motion of objects under the influence of forces. It plays a crucial role in understanding concepts like free fall, projectile motion, and the behavior of objects in various types of motion.
Formula for Calculating Acceleration: Understanding the Basics
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. Velocity is the rate of change of position. Therefore, acceleration is the rate of change of the rate of change of position. This can be expressed mathematically as follows:
a = Δv / Δt
where:
- a is acceleration
- Δv is the change in velocity
- Δt is the change in time
Key Variables and Equations for Acceleration Calculations
The key variables in the acceleration formula are:
- Final velocity (vf): The velocity of the object at the end of the time interval.
- Initial velocity (vi): The velocity of the object at the beginning of the time interval.
- Acceleration (a): The rate of change of velocity.
- Time (t): The amount of time it takes for the velocity to change.
The equation for calculating acceleration can be rearranged to solve for any of the other variables, as follows:
- vf = vi + at
- vi = vf - at
- t = Δv / a
Practical Applications of the Acceleration Formula
The acceleration formula can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as:
- Calculating the acceleration of a car as it speeds up or slows down.
- Calculating the acceleration of a projectile as it is fired into the air.
- Calculating the acceleration of a falling object.
- Calculating the acceleration of a roller coaster as it goes up and down hills.
Examples
Here are some examples of how the acceleration formula can be used to solve practical problems:
- A car accelerates from 0 mph to 60 mph in 10 seconds. What is the car's acceleration?
a = Δv / Δt
a = (60 mph - 0 mph) / 10 s
a = 6 mph/s
- A projectile is fired into the air with an initial velocity of 100 m/s. What is the acceleration of the projectile due to gravity?
a = -9.8 m/s²
- A falling object accelerates due to gravity at a rate of 9.8 m/s². If the object is dropped from a height of 100 m, how long will it take to reach the ground?
t = √(2h / a)
t = √(2 * 100 m / 9.8 m/s²)
t = 4.52 s
- A roller coaster goes up a hill with an acceleration of 2 m/s². If the roller coaster starts at the bottom of the hill with a velocity of 10 m/s, how long will it take to reach the top of the hill?
vf = vi + at
0 = 10 m/s + 2 m/s² * t
t = -5 s
The acceleration formula is a powerful tool that can be used to solve a variety of problems in physics and engineering. By understanding the basics of the acceleration formula, you can apply it to solve real-world problems.