What does the atomic mass for each element actually represent?
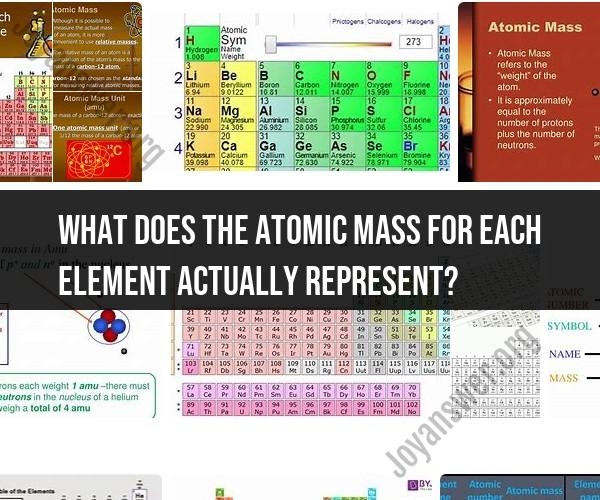
The atomic mass, also known as the atomic weight, for each chemical element represents the weighted average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of that element relative to the mass of carbon-12 (12C). It is typically expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or unified atomic mass units (u), where 1 atomic mass unit is approximately equal to the mass of a proton or a neutron.
Here's a breakdown of what the atomic mass for each element actually represents:
Isotopic Composition: Most elements exist in nature as a mixture of different isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons (and, therefore, the same chemical properties) but a different number of neutrons. These isotopes can have slightly different masses.
Weighted Average: The atomic mass takes into account the abundance of each naturally occurring isotope of the element. Since different isotopes occur in different proportions, the atomic mass is a weighted average that reflects the most common isotopes more heavily.
Relative to Carbon-12: The atomic mass is reported relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Carbon-12 is chosen as the reference because it is one of the most abundant isotopes of carbon and has a defined mass of exactly 12 atomic mass units.
Mass Number: The atomic mass is sometimes referred to as the mass number (though they are not precisely the same thing). The mass number of an element is the whole number nearest to its atomic mass. For example, the atomic mass of hydrogen is approximately 1.008 u, so its mass number is often rounded to 1.
Units: Atomic mass units (amu) or unified atomic mass units (u) are the units used for atomic mass. These units are convenient because they are approximately equal to the mass of a proton or neutron.
Molar Mass: The atomic mass can also be expressed in grams per mole (g/mol) and is known as the molar mass. It tells you the mass of one mole (6.022 x 10^23) of atoms of that element. For elements, the molar mass is numerically equal to the atomic mass in atomic mass units.
In summary, the atomic mass represents the average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element, taking into account their relative abundance. It is a fundamental property of an element and is used extensively in chemistry for stoichiometry, calculating quantities of substances in chemical reactions, and determining the formula weights of compounds.