What two factors determine the atomic mass of an element?
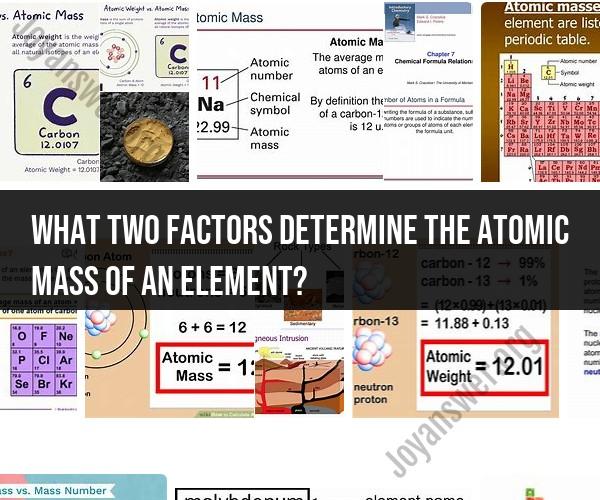
The atomic mass of an element is determined by two main factors:
Protons and Neutrons: The atomic mass of an element is primarily determined by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Protons and neutrons are both subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. Together, the sum of protons and neutrons is known as the atomic mass number (also called mass number or nucleon number).
For example, if an atom has 6 protons and 6 neutrons in its nucleus, its atomic mass number will be 12. This corresponds to the element carbon (C), which has an atomic mass of approximately 12 atomic mass units (amu).
Electrons: Electrons, the negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus, also have mass, but their mass is much smaller compared to protons and neutrons. In most cases, the contribution of electrons to the overall atomic mass of an element is negligible when compared to the combined mass of protons and neutrons. Therefore, the atomic mass of an element is primarily determined by the nucleus's composition of protons and neutrons.
It's important to note that the atomic mass of an element is often expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or unified atomic mass units (u), which are units of measurement for atomic and molecular masses. The atomic mass of an element is typically found on the periodic table and represents the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of that element, taking into account their relative abundance. Isotopes are variants of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, resulting in different atomic masses.