What are Treasury yields and why do they matter?
Treasury yields refer to the interest rates or returns earned by investors on U.S. government debt securities, specifically Treasury bonds, Treasury notes, and Treasury bills. These yields are the annualized percentage rates paid to investors who purchase these government securities.
Here's an explanation of Treasury yields and their economic significance:
1. Types of U.S. Government Debt Securities:
- Treasury Bills (T-bills): Short-term securities with maturities of one year or less.
- Treasury Notes (T-notes): Medium-term securities with maturities ranging from two to ten years.
- Treasury Bonds (T-bonds): Long-term securities with maturities exceeding ten years.
2. Calculation of Treasury Yields:
- Treasury yields are expressed as a percentage of the face value of the security.
- They are calculated based on the difference between the purchase price of the security and its face value, considering the periodic interest payments made to investors.
3. Economic Significance of Treasury Yields:
Indicator of Interest Rates: Treasury yields serve as a benchmark for interest rates across the financial markets. Changes in Treasury yields often influence other interest rates, including mortgage rates, corporate bond yields, and savings account rates.
Risk-Free Rate: U.S. Treasuries are considered one of the safest investments because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. Treasury yields are often used as the risk-free rate of return in financial models and valuations.
Investor Sentiment: Changes in Treasury yields can reflect investor sentiment and economic expectations. For example, rising yields may indicate expectations of higher inflation or economic growth, while falling yields may suggest concerns about economic stability.
Impact on Financial Markets: Treasury yields can impact the performance of various financial assets. When yields rise, the prices of existing bonds with lower yields may fall, leading to losses for bondholders. Conversely, falling yields can boost bond prices.
Federal Reserve Policy: Treasury yields can influence the monetary policy decisions of the Federal Reserve. The central bank may adjust its benchmark interest rates (e.g., the federal funds rate) in response to economic conditions and Treasury yields.
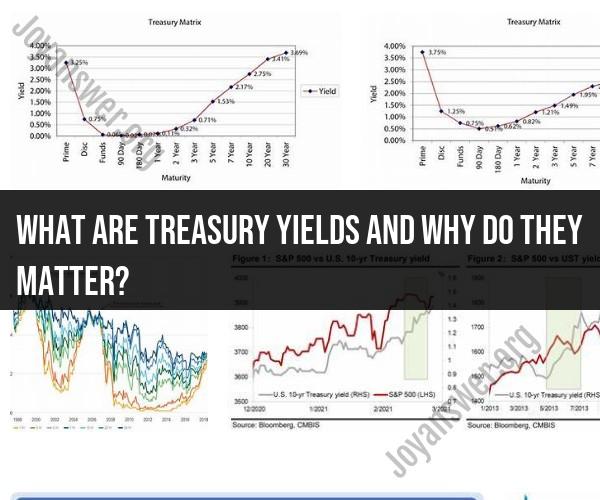
Yield Curve: The yield curve, which plots the yields of Treasury securities across various maturities, can provide insights into the state of the economy. An upward-sloping yield curve (long-term yields higher than short-term yields) is often associated with economic expansion, while an inverted yield curve (short-term yields higher than long-term yields) may signal a possible recession.
4. Yield Inversions and Economic Indicators:
- An inverted yield curve, where short-term Treasury yields exceed long-term yields, has historically been a reliable indicator of an impending economic recession. Policymakers and investors closely monitor yield curve dynamics for this reason.
In summary, Treasury yields are critical financial indicators with far-reaching implications. They reflect the government's borrowing costs, influence interest rates throughout the economy, and provide valuable information about economic conditions and investor sentiment. For these reasons, Treasury yields are closely watched by financial professionals, policymakers, and economists as a barometer of economic health and stability.