Are these things abiotic or biotic?
The terms "abiotic" and "biotic" are used to distinguish between living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) elements in an ecosystem. Here's a brief explanation of each:
Abiotic:
- Definition: Abiotic factors refer to non-living components in an ecosystem. These elements are essential for the functioning of the environment but do not have biological origins.
- Examples:
- Temperature
- Sunlight
- Soil
- Water
- Air
- Minerals
- Rocks
Biotic:
- Definition: Biotic factors are living components in an ecosystem. These elements are derived from living organisms and play a crucial role in the overall balance of the ecosystem.
- Examples:
- Plants
- Animals
- Fungi
- Bacteria
- Protists
- Viruses
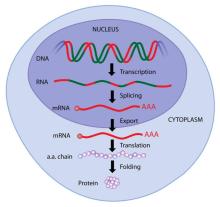
In summary, abiotic elements are non-living factors, while biotic elements are living organisms. Understanding the distinction between abiotic and biotic factors is fundamental in ecology and environmental science for studying the interactions and dynamics within ecosystems.
Unfortunately, you haven't provided any specific things for me to categorize as abiotic or biotic. Please provide a list of items or examples you'd like me to classify, and I'll be happy to help!
Generally, scientists categorize elements in an ecosystem as abiotic or biotic based on their origin and characteristics:
Abiotic factors:
- Non-living components: Include physical characteristics and chemical substances of an environment.
- Examples: Temperature, sunlight, water, air, rocks, minerals, soil, wind, fire.
Biotic factors:
- Living organisms: Include all living things within an ecosystem.
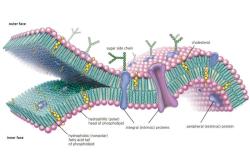
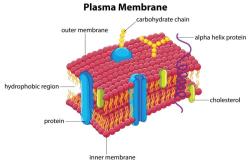
- Examples: Plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, protists.
- There can be some gray areas, where elements exhibit characteristics of both abiotic and biotic components:
- Viruses: Considered non-living as they lack cellular structure and independent metabolism, but rely on living hosts to replicate.
- Fossil fuels: Formed from decomposed organic matter (once biotic), now considered abiotic as they lack life processes.
- Enzymes: Produced by living organisms but act as non-living catalysts in chemical reactions.
In these cases, the specific context and function of the element determine its classification within the ecosystem.
If you provide specific examples, I can give you a more precise answer about whether they are considered abiotic or biotic.