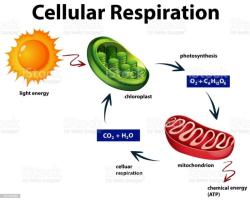
What is the correct sequence of cellular respiration?
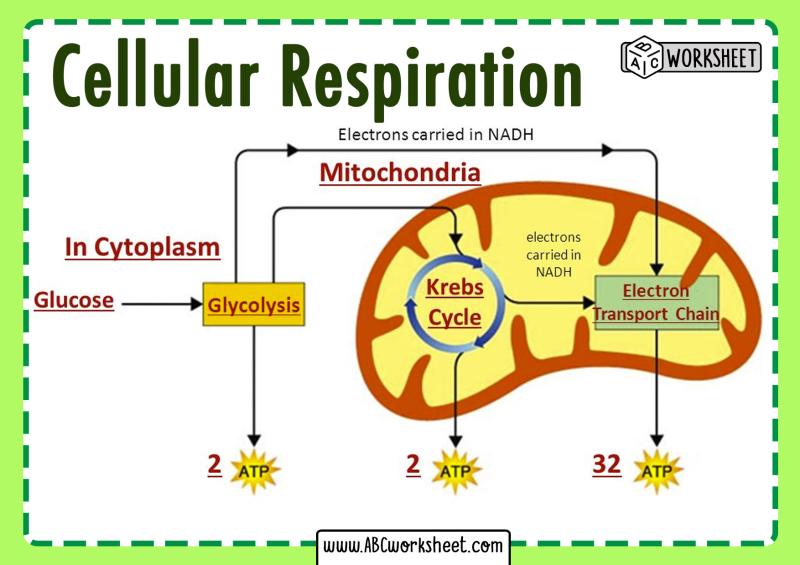
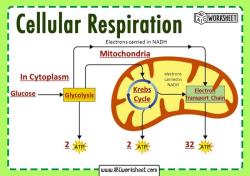
Cellular respiration is a process that takes place in cells to convert nutrients into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The correct sequence of cellular respiration involves several stages, including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (also known as the Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation (which includes the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis). Here is the correct order:
Glycolysis:
- Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- Glucose, a six-carbon sugar, is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, a three-carbon compound.
- ATP and NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) are produced during glycolysis.
Pyruvate Decarboxylation (Link Reaction):
- In eukaryotic cells, before entering the citric acid cycle, each pyruvate molecule undergoes decarboxylation and forms acetyl CoA. This step occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle):
- Acetyl CoA enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Through a series of chemical reactions, citric acid is formed and broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and transferring electrons to carrier molecules (NADH and FADH2).
- The citric acid cycle completes the breakdown of glucose, generating ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Oxidative Phosphorylation:
- This stage occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane and consists of two main components: the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
a. Electron Transport Chain (ETC):
- Electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 are transferred through a series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- As electrons move through the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
b. Chemiosmosis:
The proton gradient created by the electron transport chain is used to generate ATP.
Protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase, a complex enzyme, driving the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is oxygen, forming water when it accepts electrons and protons.
In summary, the correct sequence of cellular respiration is Glycolysis → Pyruvate Decarboxylation (Link Reaction) → Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle) → Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis). This process maximizes the extraction of energy from glucose molecules and produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2, which are essential for cellular functions.
What is the accurate sequence of steps in cellular respiration?
The accurate sequence of steps in cellular respiration is as follows:
- Glycolysis: This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and breaks down one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate.
- Pyruvate oxidation: This process occurs in the mitochondrial matrix and converts pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, a two-carbon molecule.
- Citric acid cycle: Also known as the Krebs cycle, this process takes place in the mitochondrial matrix and releases carbon dioxide and high-energy electrons from acetyl-CoA.
- Electron transport chain: This process occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane and transfers the high-energy electrons from the citric acid cycle to oxygen, generating ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the cell's energy currency.
- Oxidative phosphorylation: This process is the final step of cellular respiration and occurs alongside the electron transport chain. It generates ATP by using the energy released from the electron transport chain to pump protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
How is the sequence of cellular respiration processes ordered?
The sequence of cellular respiration processes is ordered in a way that allows the cell to maximize the energy it can extract from glucose. Glycolysis occurs first because it is a relatively simple process that can be carried out without oxygen. The pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle then follow, releasing carbon dioxide and high-energy electrons that are used in the electron transport chain to generate ATP. Finally, oxidative phosphorylation couples ATP synthesis to the electron transport chain, ensuring that the cell extracts the maximum amount of energy from glucose.
Are there distinct stages or phases within the cellular respiration sequence?
Yes, cellular respiration can be divided into four distinct stages or phases:
- Glycolysis: This stage occurs in the cytoplasm and does not require oxygen.
- Pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle: These stages occur in the mitochondrial matrix and require oxygen.
- Electron transport chain: This stage occurs on the inner mitochondrial membrane and requires oxygen.
- Oxidative phosphorylation: This stage occurs alongside the electron transport chain and requires oxygen.
Each stage of cellular respiration plays a crucial role in extracting energy from glucose and generating ATP, the cell's energy currency.