What are the products of cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
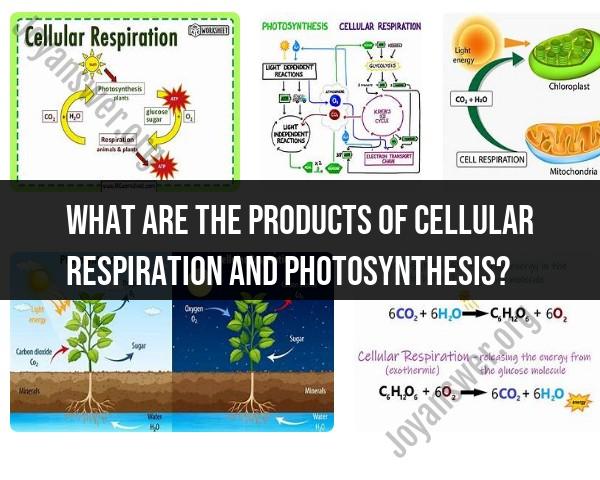
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are two interrelated biological processes that involve the exchange of energy and materials in living organisms. The products of these processes are closely linked:
Products of Cellular Respiration:
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells break down glucose and other organic molecules to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The primary products of cellular respiration are:
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): ATP is the primary energy currency of cells. It stores and releases energy for various cellular functions.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): During cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are oxidized, leading to the release of carbon dioxide as a waste product.
Water (H2O): Some water molecules are produced as a result of the chemical reactions that occur during cellular respiration.
Heat Energy: A significant amount of heat energy is generated as a byproduct of cellular respiration. While not typically harnessed by cells, it contributes to the overall increase in temperature associated with metabolic processes.
Products of Photosynthesis:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose and other organic molecules. The primary products of photosynthesis are:
Glucose (C6H12O6): Glucose is a carbohydrate that serves as the primary energy source for plants and is stored for later use. It can also be transported throughout the plant to provide energy for growth and various metabolic processes.
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is a byproduct of photosynthesis. It is released into the atmosphere, and it is essential for respiration in most organisms, including animals.
Water (H2O): Water is a reactant in the photosynthesis process. During the light-dependent reactions, water molecules are split, releasing oxygen and providing electrons for the formation of glucose.
Chemical Energy (ATP and NADPH): Photosynthesis produces ATP and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate) as energy carriers. These molecules store the energy derived from sunlight and are used in the synthesis of glucose and other organic compounds.
The relationship between cellular respiration and photosynthesis is often described as a cycle. In cellular respiration, organisms, including humans and animals, use glucose and oxygen to produce ATP, carbon dioxide, and water. The carbon dioxide produced in respiration is taken up by plants during photosynthesis, where it is converted into glucose and oxygen using light energy. This exchange of energy and materials sustains life on Earth and is fundamental to the carbon and energy cycles in ecosystems.
Products of Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis: A Comparison
Cellular respiration:
- Produces energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
- Releases carbon dioxide and water
- Occurs in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria of cells
Photosynthesis:
- Produces oxygen
- Consumes carbon dioxide and water
- Occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells
Cellular Respiration: Energy Production in Living Organisms
Cellular respiration is the process by which living organisms convert glucose into energy in the form of ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell and is used to power all cellular processes.
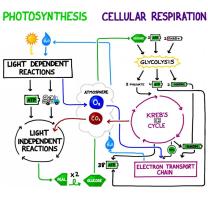
Cellular respiration occurs in three main stages:
- Glycolysis: Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell and does not require oxygen. In glycolysis, glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, producing two molecules of ATP in the process.
- Krebs cycle: The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria of the cell and requires oxygen. In the Krebs cycle, pyruvate is broken down into carbon dioxide and water, producing ATP in the process.
- Electron transport chain: The electron transport chain also takes place in the mitochondria of the cell and requires oxygen. In the electron transport chain, electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, producing ATP in the process.
Photosynthesis: The Conversion of Light into Energy
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and glucose. Glucose is a type of sugar that plants use for energy and that animals eat for food.
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages:
- Light-dependent reactions: The light-dependent reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts. In the light-dependent reactions, sunlight is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The oxygen is released into the atmosphere, and the hydrogen is used to produce ATP and NADPH.
- Calvin cycle: The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. In the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide is used to produce glucose using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions.
Interdependence of Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are interdependent processes. Cellular respiration requires oxygen, which is a product of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide, which is a product of cellular respiration.
The Global Significance of Respiration and Photosynthesis
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are essential for life on Earth. Cellular respiration produces the energy that all living organisms need to function. Photosynthesis produces the oxygen that all living organisms need to breathe.
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis also play a role in the climate. Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that traps heat, contributing to global warming. Photosynthesis consumes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to mitigate global warming.
Overall, cellular respiration and photosynthesis are two of the most important processes on Earth. They are essential for life on Earth and play a role in the climate.