What is the general formula for cellular respiration?
The general formula for cellular respiration is often represented as:
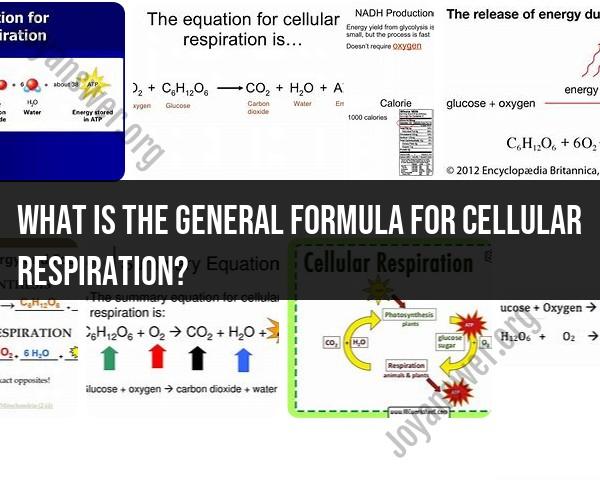
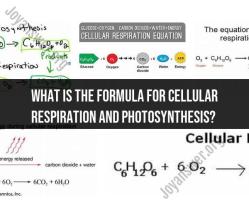
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 (oxygen) → 6CO2 (carbon dioxide) + 6H2O (water) + Energy (ATP)
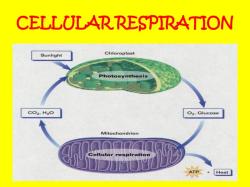
This formula represents the overall process of cellular respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria of cells and involves the breakdown of glucose to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The process consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation.
In summary, during cellular respiration:
- Glucose (C6H12O6) is oxidized and broken down.
- Oxygen (O2) is utilized as an electron acceptor.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) are produced as byproducts.
- ATP is generated, providing the cell with the energy needed for various cellular processes.
The actual biochemical pathways involved in cellular respiration are complex and involve numerous intermediate steps, enzymes, and electron carriers. However, the general formula provides an overview of the inputs and outputs of this vital metabolic process that generates energy for cells.
1. General Formula for Cellular Respiration
The general formula for cellular respiration represents the overall chemical reaction that takes place in cells to convert glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) into energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The simplified formula can be written as:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP + energy
In this formula, glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is the substrate, oxygen (O₂) is the electron acceptor, and carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and ATP are the products. The formula also indicates that energy is released during the process.
2. Formulaic Representation of Cellular Respiration
The formula for cellular respiration can be further broken down to represent the different stages of the process:
Glycolysis:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 2ADP + 2Pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2H+
Pyruvate Oxidation:
Pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA → acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO₂
Krebs Cycle:
Acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + ADP + Pi + FAD → 2 CO₂ + GTP + NADH + FADH₂
Electron Transport Chain:
NADH + FADH₂ + O₂ → H₂O + ATP
These formulas provide a simplified representation of the complex biochemical reactions involved in cellular respiration.
3. Variations in the Formula across Different Stages
The formula for cellular respiration remains constant across the different stages, representing the overall conversion of glucose into ATP. However, the specific molecules and their quantities vary depending on the stage. For instance, glycolysis produces only a small amount of ATP (2 molecules), while the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain generate a significant proportion of ATP (about 34 and 26 molecules, respectively).
The formula also highlights the involvement of different electron carriers, such as NADH and FADH₂, which transport electrons from the breakdown of glucose to the final electron acceptor, oxygen. These electrons are eventually used to generate ATP through the electron transport chain.
The simplified formula serves as a concise representation of the overall process of cellular respiration, summarizing the conversion of glucose into ATP and energy.