What it the correct equation for average velocity?
The correct equation for average velocity is:
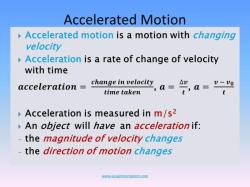
Average Velocity (V_avg) = (Change in Displacement) / (Change in Time)
Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
V_avg = (Δx) / (Δt)
Where:
- V_avg is the average velocity.
- Δx (delta x) is the change in displacement (the final position minus the initial position).
- Δt (delta t) is the change in time (the final time minus the initial time).
Average velocity represents the overall displacement of an object divided by the total time taken to achieve that displacement. It provides information about an object's overall motion over a certain period, taking into account its starting and ending positions. Average velocity is typically expressed in units of distance per time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h), depending on the unit system being used.
Calculating Average Velocity: The Correct Equation
Average velocity (v̄) is defined as the total displacement (Δx) divided by the total time interval (Δt):
v̄ = Δx / Δt
This formula applies to both one-dimensional and two-dimensional motion.
Variables and Units in Average Velocity Formulas
Displacement (Δx): The change in position of an object. The units of displacement are typically meters (m), kilometers (km), or feet (ft).
Time Interval (Δt): The total time elapsed during the motion. The units of time interval are typically seconds (s), minutes (min), or hours (hr).
Average Velocity (v̄): The rate of change of an object's position over time. The units of average velocity are meters per second (m/s), kilometers per hour (km/h), or feet per second (ft/s).
Examples and Practice Problems for Average Velocity
Example 1: A car travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours. What is its average velocity?
v̄ = Δx / Δt = 100 km / 2 hr = 50 km/hr
Example 2: A ball is thrown vertically upwards and reaches a maximum height of 20 meters before falling back down. The total time it takes for the ball to reach the ground is 5 seconds. What is the average velocity of the ball?
Δx = 20 m (upward displacement) + 20 m (downward displacement) = 40 m
Δt = 5 s
v̄ = Δx / Δt = 40 m / 5 s = 8 m/s
Applications of Average Velocity in Physics
Average velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the study of motion. It is used to describe the overall speed and direction of an object's motion over a given time interval. Average velocity is often contrasted with instantaneous velocity, which is the velocity of an object at a specific point in time.
Significance of Average Velocity in Kinematics
Average velocity is important for understanding various aspects of motion, including:
Comparing the motion of different objects: Average velocity allows us to compare the speed of different objects moving along the same path or in different directions.
Calculating the distance traveled: Average velocity can be used to calculate the total distance traveled by an object over a given time interval.
Analyzing the overall motion of an object: Average velocity provides a general overview of an object's motion, indicating its overall speed and direction over a period of time.