How do you calculate the average acceleration?
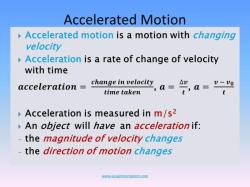
Average acceleration is calculated by determining the change in velocity over a specific time period. The formula for average acceleration is:
Where:
- is the average acceleration.
- is the change in velocity.
- is the change in time.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to calculate average acceleration:
Step 1: Determine the Initial Velocity (v1) and Final Velocity (v2):
- You'll need to know the initial velocity (v1) and the final velocity (v2) of the object. Make sure the units for velocity are consistent (e.g., meters per second, miles per hour).
Step 2: Calculate the Change in Velocity (Δv):
- The change in velocity () is the difference between the final velocity (v2) and the initial velocity (v1).
Step 3: Determine the Initial Time (t1) and Final Time (t2):
- You need to know the initial time (t1) and the final time (t2) during which the change in velocity occurred. Make sure the units for time are consistent (e.g., seconds).
Step 4: Calculate the Change in Time (Δt):
- The change in time () is the difference between the final time (t2) and the initial time (t1).
Step 5: Use the Formula for Average Acceleration:
- Plug the values of and into the formula for average acceleration:
Step 6: Calculate and Express the Result:
- Perform the division to find the average acceleration. Make sure to include units (e.g., m/s² or km/h²) to specify the acceleration's measurement.
The result represents the average acceleration of the object over the specified time period. Average acceleration is a measure of how velocity changes over time, and it's commonly used in physics and engineering to describe the motion of objects.
How to calculate average acceleration in physics?
To calculate average acceleration in physics, you can use the following formula:
Average acceleration = (Final velocity - Initial velocity) / Time
This formula can be used to calculate the average acceleration of any object, regardless of its motion.
What is the formula for finding the average acceleration of an object?
The formula for finding the average acceleration of an object is the same as the formula for calculating average acceleration in physics:
Average acceleration = (Final velocity - Initial velocity) / Time
How do you interpret the results of an average acceleration calculation?
The results of an average acceleration calculation can be interpreted in a few different ways. For example, if the average acceleration is positive, it means that the object is speeding up. If the average acceleration is negative, it means that the object is slowing down. And if the average acceleration is zero, it means that the object is moving at a constant velocity.
What units are commonly used to express acceleration in scientific measurements?
The most common unit of acceleration in scientific measurements is meters per second squared (m/s^2). Other units of acceleration include feet per second squared (ft/s^2) and miles per hour squared (mph^2).
Can you provide real-world examples of calculating average acceleration?
Here are a few real-world examples of calculating average acceleration:
- A car accelerates from 0 to 60 mph in 6 seconds. The average acceleration of the car is 10 mph/s.
- A ball is thrown up into the air and reaches a maximum height of 10 meters. The average acceleration of the ball on its way up is -9.81 m/s^2 (negative because the ball is slowing down).
- A roller coaster accelerates from 0 to 60 mph in 5 seconds. The average acceleration of the roller coaster is 12 mph/s.
Calculating average acceleration can be useful in a variety of situations. For example, it can be used to design vehicles, track the motion of objects, and predict the future behavior of objects.