How are the financial statements prepared?
The process of preparing financial statements involves several steps, and it typically follows a specific order. Here's an overview of how financial statements are prepared:
Gather Financial Data:
- Start by collecting all the financial data and records relevant to the reporting period. This includes transaction records, ledgers, income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and any supporting documentation.
Adjusting Entries:
- Review the financial data and make adjusting entries to ensure that the accounts accurately reflect the company's financial position. Common adjustments include depreciation, accruals, prepayments, and allowances for bad debts.
Prepare Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement):
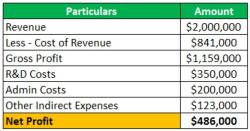
- The income statement shows the company's revenues and expenses during a specific period, resulting in either a net profit or loss. It typically includes sections for revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, other income or expenses, and net income.
Prepare Balance Sheet:
- The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company's financial position at a specific point in time. It lists assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. Assets are usually categorized as current (e.g., cash, accounts receivable) or non-current (e.g., property, plant, equipment).
Prepare Cash Flow Statement:
- The cash flow statement shows the company's cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities during the reporting period. It reconciles the beginning and ending cash balances.
Prepare Statement of Changes in Equity (if applicable):
- Some companies include a statement of changes in equity, which explains changes in shareholders' equity during the reporting period. It reflects transactions such as issuing or repurchasing shares and dividend payments.
Disclosures and Notes:
- Provide necessary disclosures and footnotes to the financial statements to explain significant accounting policies, assumptions, and contingencies. These notes ensure transparency and compliance with accounting standards.
Review and Audit (if required):
- Depending on regulatory requirements and the company's size, the financial statements may undergo review or audit by external auditors. The auditor's opinion adds credibility to the financial statements.
Finalize Financial Statements:
- Once the financial statements are complete and any necessary adjustments are made, finalize the statements for distribution and use. Ensure that they comply with relevant accounting standards (e.g., GAAP or IFRS).
Approval and Release:
- The financial statements are typically reviewed and approved by the company's management or board of directors. After approval, they are released to shareholders, investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities.
Publish and Share:
- Share the financial statements with relevant stakeholders, such as investors, creditors, and government agencies. Publicly traded companies are required to file their financial statements with regulatory authorities like the SEC in the United States.
Use for Decision-Making:
- Stakeholders use the financial statements for various purposes, including investment decisions, credit assessments, and evaluating the company's financial health.
It's important to note that financial statement preparation must adhere to accounting principles and standards applicable in the company's jurisdiction, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). The level of detail and complexity of financial statements can vary based on the size and nature of the organization.