What does inferior wall myocardial infarction stand for?
An inferior wall myocardial infarction is a medical term that refers to a specific type of heart attack. Let's break down the terminology:
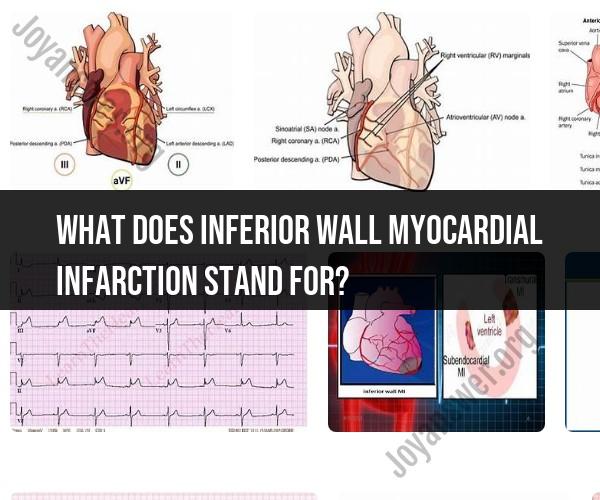
Inferior Wall: This part of the term refers to the location of the heart where the myocardial infarction (heart attack) has occurred. The heart is often divided into walls or regions for diagnostic and treatment purposes. The inferior wall is the lower part of the heart.
Myocardial Infarction: This is the medical term for a heart attack. It occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle (myocardium) is blocked, typically due to a clot in one of the coronary arteries. Without an adequate blood supply, the affected heart muscle can become damaged or die.
So, an "inferior wall myocardial infarction" specifically indicates that the heart attack has occurred in the lower part of the heart muscle. The location of a heart attack can have different clinical implications and may influence treatment decisions in cardiology.
Understanding Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction (MI)
An inferior wall myocardial infarction (MI), also known as an inferior wall heart attack, is a type of heart attack that occurs when the blood supply to the inferior wall of the heart is blocked. The inferior wall is the bottom part of the heart.
Location and Anatomy of the Heart's Inferior Wall
The heart is made up of four chambers: the left atrium, the left ventricle, the right atrium, and the right ventricle. The inferior wall of the heart is located on the bottom of the left ventricle. It is supplied with blood by the right coronary artery.
Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis of Inferior Wall MI
The most common cause of inferior wall MI is a blood clot blocking the right coronary artery. This can happen due to atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up on the walls of the arteries. Other causes of inferior wall MI include:
- Coronary artery spasm
- Coronary artery dissection
- Embolism (a blood clot that travels to the heart from another part of the body)
- Cocaine use
- Severe anemia
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
The symptoms of inferior wall MI are similar to those of other types of heart attacks. They can include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Lightheadedness
- Fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Inferior wall MI is diagnosed based on a patient's symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Tests that may be used to diagnose inferior wall MI include:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG)
- Echocardiogram
- Blood tests
- Cardiac catheterization
Medical Interventions and Treatment for MI
The goal of treatment for inferior wall MI is to restore blood flow to the heart muscle and to prevent further damage. This may involve the following:
- Medications to dissolve blood clots (thrombolytics)
- Medications to widen the arteries (angioplasty and stenting)
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery
Recovery and Lifestyle Changes After Inferior Wall MI
After an inferior wall MI, it is important to make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk of having another heart attack. These changes include:
- Quitting smoking
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Controlling your blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Managing stress
It is also important to follow your doctor's instructions carefully and to take all of your medications as prescribed.