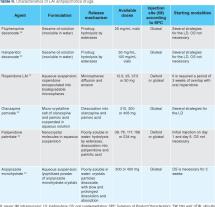
Can atypical antipsychotics be used in adults?
Yes, atypical antipsychotics are commonly used in adults for the treatment of various mental health conditions. Atypical antipsychotics, also known as second-generation antipsychotics, differ from older, first-generation antipsychotics in their pharmacological profiles and side effect profiles.
Here are some of the conditions for which atypical antipsychotics may be prescribed in adults:
Schizophrenia: Atypical antipsychotics are often the first-line treatment for schizophrenia. They can help manage symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
Bipolar Disorder: Atypical antipsychotics are used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, both in the acute manic or mixed episodes and for maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Major Depressive Disorder (with psychotic features): In some cases of major depression with psychotic features, atypical antipsychotics may be added to an antidepressant to help manage psychotic symptoms.
Augmentation in Treatment-Resistant Depression: Atypical antipsychotics may be used as an augmentation strategy when standard antidepressants alone are not effective in treating depression.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (off-label): Some atypical antipsychotics may be used off-label to augment treatment in generalized anxiety disorder.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) (off-label): In certain cases, atypical antipsychotics may be used off-label to help manage symptoms of PTSD.
Insomnia (off-label): Some atypical antipsychotics, due to their sedative properties, may be used off-label to treat insomnia.
It's important to note that the use of atypical antipsychotics should be carefully monitored by a healthcare professional due to potential side effects. These medications can have a range of side effects, including weight gain, metabolic effects, and increased risk of diabetes. The choice of medication and dosage will depend on the specific diagnosis, individual patient characteristics, and the presence of any other medical conditions.
Patients should discuss the potential benefits and risks of atypical antipsychotic medications with their healthcare provider, and regular follow-up appointments are important to monitor for side effects and adjust treatment as needed.
Are atypical antipsychotics suitable for use in adults?
Atypical antipsychotics are a class of medications that are used to treat a variety of psychiatric conditions, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. They are generally considered to be more effective than older antipsychotics, and they have a lower risk of causing extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), which are movement disorders that can be a serious side effect of antipsychotic medications.
Atypical antipsychotics can be used safely and effectively in adults, but it is important to weigh the risks and benefits carefully. The decision of whether or not to prescribe an atypical antipsychotic should be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient's individual needs and circumstances.
What are the considerations when using atypical antipsychotics in adult patients?
There are several factors to consider when prescribing atypical antipsychotics to adult patients. These include:
- The severity of the patient's symptoms: Atypical antipsychotics are most effective for treating severe psychiatric symptoms. They may not be as helpful for mild symptoms.
- The patient's overall health: Atypical antipsychotics can interact with other medications, so it is important to be aware of the patient's other medical conditions and medications.
- The patient's age: Atypical antipsychotics may have different risks and side effects in older adults.
- The patient's preferences: It is important to involve the patient in the decision-making process and to take their preferences into account.
How effective are atypical antipsychotics in treating adult psychiatric conditions?
Atypical antipsychotics are generally effective in treating a variety of adult psychiatric conditions. They are particularly effective for treating the positive symptoms of schizophrenia, such as hallucinations and delusions. They can also be effective for treating the negative symptoms of schizophrenia, such as social withdrawal and apathy.
Atypical antipsychotics are also effective in treating bipolar disorder. They can help to prevent and treat manic episodes, and they can also help to stabilize mood and reduce depressive symptoms.
Atypical antipsychotics are sometimes used to treat major depressive disorder, but they are not considered to be a first-line treatment. They may be used in combination with other medications, such as antidepressants, for patients who do not respond to antidepressants alone.
Overall, atypical antipsychotics are a valuable tool for treating a variety of adult psychiatric conditions. They are generally safe and effective, but it is important to weigh the risks and benefits carefully and to monitor patients closely for side effects.