What causes autoimmune disease?
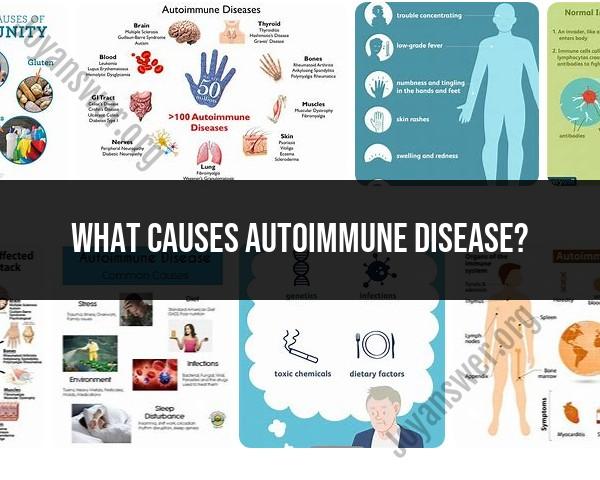
Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the body's own tissues and organs. The exact causes of autoimmune diseases are not fully understood, and they likely involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Here are some key factors that may contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases:
Genetic Factors: There is a genetic predisposition to many autoimmune diseases. Certain genes can increase the risk of developing an autoimmune condition. However, having these genetic risk factors does not guarantee that a person will develop the disease. It often takes the interplay of other factors for autoimmune diseases to manifest.
Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors have been implicated as triggers for autoimmune diseases. These triggers can include infections (such as viruses or bacteria), exposure to certain chemicals, toxins, or drugs, and even dietary factors. For example, some autoimmune diseases have been associated with specific infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sclerosis.
Immunological Factors: Dysregulation of the immune system is a central feature of autoimmune diseases. In some cases, the immune system fails to recognize "self" from "non-self," leading to an attack on the body's own tissues. In other cases, the immune system's regulatory mechanisms may not function properly.
Hormonal Factors: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, can influence the development and severity of autoimmune diseases. Many autoimmune diseases are more common in women and often show patterns related to hormonal changes, such as during pregnancy or menopause.
Gut Health: There is emerging research suggesting a link between gut health and autoimmune diseases. A disruption in the gut microbiome or increased gut permeability (leaky gut) may contribute to autoimmune disease development.
Stress: Chronic stress and emotional factors can influence the immune system and potentially contribute to the development or exacerbation of autoimmune diseases.
It's important to note that autoimmune diseases are a diverse group of conditions, and the specific causes can vary widely between different diseases. In addition, the triggers and causes may be multifactorial, meaning several factors need to come together to result in the disease.
Research in the field of autoimmune diseases is ongoing, and ongoing studies aim to better understand the underlying causes and mechanisms. Management of autoimmune diseases often involves a combination of treatments to suppress the immune system's activity and alleviate symptoms, but a cure is not typically available. Early diagnosis and effective management are crucial to improving the quality of life for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Causes and Triggers of Autoimmune Diseases
The exact cause of autoimmune diseases is unknown, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors: People with certain genes are more likely to develop autoimmune diseases. These genes may make the immune system more sensitive to triggers or less able to regulate itself.
Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors may trigger the development of an autoimmune disease in people who are genetically predisposed. These factors may include:
- Infections
- Certain medications
- Sunlight exposure
- Smoking
- Stress
- Diet
Immune System Dysregulation in Autoimmune Conditions
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body's own tissues. This can happen in a number of ways, such as:
- Autoantibodies: Autoantibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that attack the body's own tissues.
- T cells: T cells are a type of white blood cell that helps to fight infection. In autoimmune diseases, T cells can become activated and attack the body's own tissues.
- Cytokines: Cytokines are small proteins that signal to other cells of the immune system. In autoimmune diseases, cytokines can be produced in excess, which can lead to inflammation and tissue damage.
Common Autoimmune Disorders and Their Origins
Some common autoimmune disorders include:
- Lupus: Lupus is a chronic disease that can affect any part of the body. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the joints. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking and exposure to certain bacteria.
- Multiple sclerosis: Multiple sclerosis is a chronic disease that affects the central nervous system. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to certain viruses.
- Type 1 diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is a chronic disease in which the body does not produce enough insulin. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as exposure to certain viruses.
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. They are thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking and exposure to certain bacteria.
Genetic and Environmental Factors in Autoimmunity
Genetic factors: People with certain genes are more likely to develop autoimmune diseases. These genes may make the immune system more sensitive to triggers or less able to regulate itself.
Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors may trigger the development of an autoimmune disease in people who are genetically predisposed. These factors may include:
- Infections
- Certain medications
- Sunlight exposure
- Smoking
- Stress
- Diet
Advances in Research and Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases
There has been significant progress in research on autoimmune diseases in recent years. This has led to the development of new treatments that can help to manage the symptoms of autoimmune diseases and improve the quality of life for patients.
Some of the most promising advances in research on autoimmune diseases include:
- Targeted therapies: Targeted therapies are drugs that specifically target the immune cells and molecules involved in autoimmune diseases. This can help to reduce inflammation and tissue damage without harming the rest of the immune system.
- Immunosuppressants: Immunosuppressants are drugs that suppress the immune system. These drugs can be used to treat autoimmune diseases by reducing the number and activity of immune cells.
- Stem cell therapy: Stem cell therapy is a promising new approach to treating autoimmune diseases. Stem cells can be used to repair damaged tissues and replace immune cells that have been destroyed by the disease.
While there is no cure for autoimmune diseases, the advances in research and treatment have made it possible for many people with autoimmune diseases to live long and healthy lives.