Is vancomycin an antibiotic?
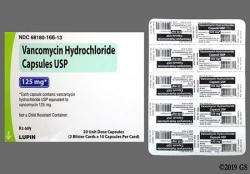
Yes, vancomycin is indeed an antibiotic. It is a potent and important antibiotic used in healthcare to treat a variety of bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Gram-positive bacteria.
Vancomycin is effective against a range of Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or MRSA), Streptococcus species, and Enterococcus species. It is often used when infections are resistant to other antibiotics or when other antibiotics are not effective.
Vancomycin is administered in various forms, including intravenous (IV) injection for systemic infections and orally for some specific intestinal infections. Due to its effectiveness and relatively low risk of causing antibiotic resistance, vancomycin is considered an essential and invaluable antibiotic in the field of healthcare, especially for treating serious bacterial infections. It plays a critical role in the treatment of many bacterial diseases, including sepsis, pneumonia, endocarditis, and skin and soft tissue infections.
It's important to note that vancomycin is used when other, less potent antibiotics are ineffective or when the infection is known to be caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. The appropriate use of vancomycin, like any antibiotic, should be determined by a healthcare professional to ensure that it is prescribed for the right infection, in the correct dose, and for the appropriate duration to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Vancomycin as an Antibiotic: An Overview
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that is used to treat serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Clostridium difficile. Vancomycin is a powerful antibiotic, and it is typically used when other antibiotics have failed.
How Vancomycin Works as an Antibiotic
Vancomycin works by inhibiting the growth and replication of bacteria. It does this by binding to the cell wall of the bacterium and preventing it from forming. This prevents the bacterium from multiplying and causing further damage to the body.
Common Uses and Administration of Vancomycin
Vancomycin is used to treat a variety of serious infections, including:
- Bone and joint infections
- Blood infections (bacteremia)
- Endocarditis (infection of the heart valves)
- Meningitis (infection of the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord)
- Pneumonia (infection of the lungs)
- Skin and soft tissue infections
- Clostridium difficile infections
Vancomycin can be administered orally or intravenously. The dosage of vancomycin depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient's age and weight.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Vancomycin is a generally safe antibiotic, but it can cause side effects, including:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Stomach upset
- Redness and swelling at the injection site (if given intravenously)
- Kidney damage
- Hearing loss
- Rashes
- Allergic reactions
Vancomycin should be used with caution in patients with kidney problems or hearing problems. Vancomycin should also be used with caution in pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers.
Alternatives and Complementary Treatments
There are a number of other antibiotics that can be used to treat gram-positive bacterial infections. Some of these antibiotics include penicillin, cephalosporins, and carbapenems.
In addition to antibiotics, there are a number of complementary treatments that can be used to treat gram-positive bacterial infections. These treatments include:
- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria that are beneficial to the gut. They can help to restore the balance of bacteria in the gut and prevent infections from recurring.
- Vitamins and minerals: A healthy diet is important for overall health and well-being. Vitamins and minerals can help to support the immune system and fight infection.
- Herbal remedies: There are a number of herbal remedies that have been shown to have antimicrobial activity. Some of these herbal remedies include garlic, echinacea, and goldenseal.
It is important to note that complementary treatments should not be used as a substitute for antibiotics. If you are thinking about using complementary treatments, talk to your doctor first.