Is vancomycin a therapeutic drug?
Yes, vancomycin is indeed a therapeutic medication. It is an antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Vancomycin is particularly effective against Gram-positive bacteria, which means it is used to treat infections caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species.
Vancomycin is typically administered intravenously, although there are oral forms available for certain conditions. It is commonly used to treat serious infections like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), endocarditis, and other severe infections that do not respond to other antibiotics.
It's important to note that vancomycin is a powerful antibiotic and is reserved for situations where other, less potent antibiotics have proven ineffective. Like all antibiotics, its use should be carefully monitored by healthcare professionals to ensure it is used appropriately and to minimize the development of antibiotic resistance. Additionally, vancomycin can have potential side effects and should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Vancomycin as a Therapeutic Drug: Uses and Benefits
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic that is used to treat a variety of serious bacterial infections, including:
- Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections
- Enterococcus infections
- Clostridium difficile infections
- Meningitis caused by Gram-positive bacteria
- Endocarditis caused by Gram-positive bacteria
- Bone and joint infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria
- Skin and soft tissue infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria
- Vancomycin is also used to prevent infections in patients who are at high risk, such as those undergoing surgery or those with weakened immune systems.
Benefits of vancomycin:
- Vancomycin is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, which means that it is effective against a wide range of bacteria.
- Vancomycin is a bactericidal antibiotic, which means that it kills bacteria.
- Vancomycin is a relatively safe antibiotic, with few side effects.
Indications and Clinical Applications of Vancomycin
Vancomycin is indicated for the treatment of the following infections:
- Endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
- Meningitis caused by Gram-positive bacteria
- Pneumonia caused by MRSA or Enterococcus faecium
- Skin and soft tissue infections caused by MRSA or Enterococcus faecium
- Bone and joint infections caused by MRSA or Enterococcus faecium
- Intra-abdominal infections caused by MRSA or Enterococcus faecium
- Bacteremia caused by MRSA or Enterococcus faecium
- C. difficile colitis
Vancomycin is also used to prevent infections in patients who are at high risk, such as those undergoing surgery or those with weakened immune systems.
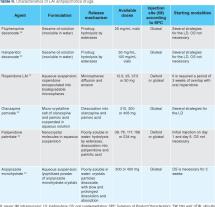
Dosage, Administration, and Monitoring of Vancomycin Therapy
Vancomycin is administered intravenously, usually over 60 minutes. The dosage of vancomycin depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the patient's weight and kidney function.
Vancomycin levels in the blood should be monitored regularly to ensure that the patient is receiving the correct dose and to prevent toxicity.
Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
The most common side effects of vancomycin are:
- Infusion-related reactions, such as fever, chills, and redness at the injection site
- Nephrotoxicity (kidney damage)
- Ototoxicity (ear damage)
- Neutropenia (low white blood cell count)
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelet count)
Vancomycin can also cause more serious side effects, such as:
- Red man syndrome (a severe allergic reaction)
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (a rare but life-threatening skin condition)
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis (a rare but life-threatening skin condition)
The Role of Vancomycin in Treating Bacterial Infections
Vancomycin is a critical antibiotic in the fight against bacterial infections. It is often used as a last-resort antibiotic for patients who have infections with bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics.
Vancomycin has played a major role in reducing the mortality rate of infections caused by MRSA. It is also used to treat infections caused by other drug-resistant bacteria, such as Enterococcus faecium and C. difficile.
Vancomycin is a valuable antibiotic, but it is important to use it wisely. Overuse of vancomycin can lead to the development of antibiotic resistance. Therefore, vancomycin should only be used when necessary and under the supervision of a doctor.