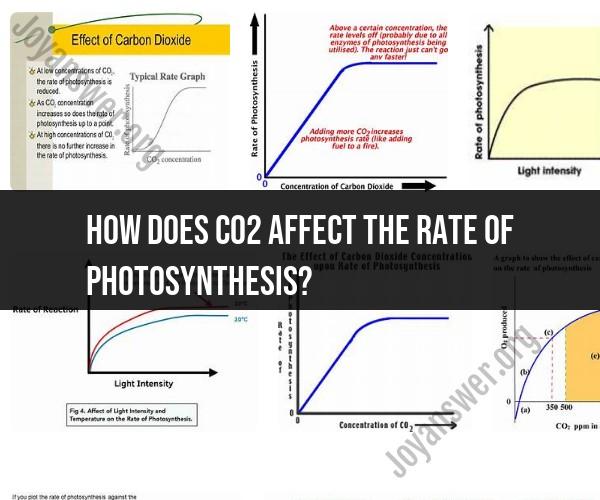
How does CO2 affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a critical factor that affects the rate of photosynthesis in plants. The level of CO2 in the surrounding environment can significantly influence the photosynthetic process. Here's how CO2 affects photosynthesis:
1. Carbon Source for Photosynthesis:
- CO2 is one of the primary reactants (carbon source) required for photosynthesis. Along with water and light energy, CO2 is used to produce glucose and other organic compounds.
- Increased CO2 levels can potentially increase the availability of this essential carbon source for plants.
2. Carbon Fixation Rate:
- The rate of photosynthesis is directly proportional to the availability of CO2. As CO2 levels rise, the rate of carbon fixation increases.
- Higher CO2 concentrations can lead to more efficient carbon fixation during photosynthesis.
3. Photosynthetic Efficiency:
- Increased CO2 levels generally enhance the photosynthetic efficiency of C3 plants. These are the majority of plants, including most crops.
- The increased availability of CO2 can lead to faster growth and increased yield in C3 plants.
4. C3 vs. C4 Plants:
- Different plant species have different photosynthetic pathways. C3 plants, like wheat and rice, initially benefit more from increased CO2 levels, resulting in increased photosynthesis rates.
- C4 plants, like maize and sugarcane, are adapted to perform photosynthesis more efficiently in low CO2 conditions. While they still benefit from higher CO2, their response may not be as dramatic as C3 plants.
5. Limiting Factor:
- In some cases, CO2 availability can be a limiting factor for photosynthesis. When other conditions like light and temperature are optimal, a shortage of CO2 can restrict the rate of photosynthesis.
- Increasing CO2 levels can alleviate this limitation and allow the plant to maximize its photosynthetic potential.
6. Water Use Efficiency:
- Elevated CO2 levels can improve the water use efficiency of plants. They can maintain their stomata (small openings in leaves) partially closed, reducing water loss through transpiration while still acquiring sufficient CO2 for photosynthesis.
7. Interactions with Other Factors:
- CO2 levels interact with other environmental factors like light intensity and temperature. The combined effect of these factors can influence the overall photosynthesis rate.
- For example, in controlled environments like greenhouses, increasing both CO2 and light levels can lead to substantial improvements in plant growth and yield.
8. Global Carbon Cycle:
- On a broader scale, the level of atmospheric CO2, influenced by human activities like the burning of fossil fuels, can have long-term effects on the Earth's climate, which, in turn, can impact plant ecosystems and their photosynthesis rates.
In summary, CO2 concentration directly affects the rate of photosynthesis by influencing the availability of carbon, which is a critical component of organic compounds produced during photosynthesis. Increased CO2 levels generally lead to enhanced photosynthetic rates, improved growth, and potentially increased crop yields, especially in C3 plants. However, the specific response to CO2 can vary among plant species and may be influenced by other environmental factors.
CO2 and Photosynthesis: Exploring the Symbiotic Relationship
Carbon dioxide (CO2) and photosynthesis have a symbiotic relationship. CO2 is the main raw material that plants use to produce glucose during photosynthesis. In turn, photosynthesis releases oxygen into the atmosphere, which is essential for respiration.
Impact of CO2 on Photosynthesis Rate: Mechanisms Unveiled
CO2 has a significant impact on the rate of photosynthesis. In general, the higher the CO2 concentration, the faster the rate of photosynthesis. This is because CO2 is the substrate for the Calvin cycle, which is the stage of photosynthesis where carbon is fixed into organic matter.
There are two main mechanisms by which CO2 affects the rate of photosynthesis:
- Increased availability of RuBP: CO2 reacts with RuBP to form PGA, which is the first stable product of the Calvin cycle. When CO2 concentrations are high, there is more RuBP available to react with CO2, which increases the rate of photosynthesis.
- Activation of RuBisCO: RuBisCO is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between CO2 and RuBP. CO2 activates RuBisCO, which increases the rate of the reaction.
The CO2 Factor in Photosynthesis: Rate and Mechanisms
The rate of photosynthesis is also affected by other factors, such as light intensity, temperature, and water availability. However, CO2 is one of the most important factors that determines the rate of photosynthesis.
In recent years, there has been growing interest in the potential to use elevated CO2 levels to increase crop yields. However, it is important to note that elevated CO2 levels can also have negative impacts, such as ocean acidification and climate change.
Conclusion
The relationship between CO2 and photosynthesis is complex and multifaceted. CO2 is essential for photosynthesis, and it has a significant impact on the rate of photosynthesis. However, elevated CO2 levels can also have negative impacts. It is important to carefully consider the potential benefits and risks before using elevated CO2 levels to increase crop yields.