What is identification and authentication access controls?
Identification and authentication access controls are crucial components of information security that help enhance the security of systems, networks, and data. These controls verify the identity of users and ensure that only authorized individuals gain access to protected resources. Here's an overview of identification and authentication access controls and how they enhance security:
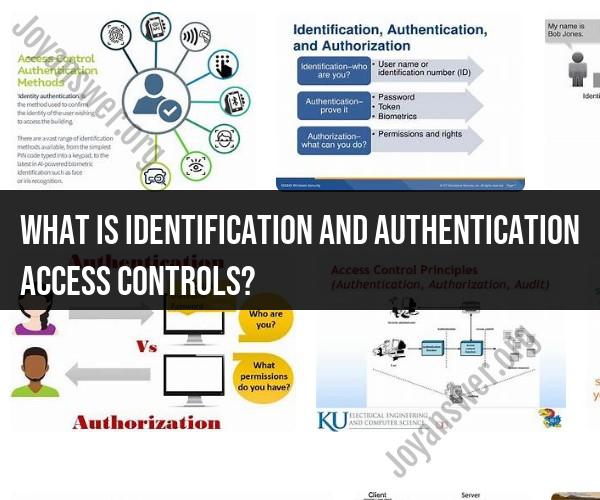
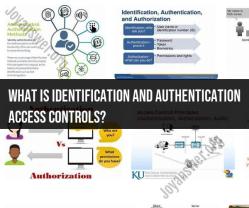
Identification:
- Definition: Identification is the process by which a user claims or provides a unique identifier, such as a username, email address, or employee ID, to access a system or application.
- Enhanced Security: Identification helps establish accountability by associating actions or access requests with specific user identities. It forms the basis for further authentication.
Authentication:
- Definition: Authentication is the process of verifying the claimed identity of a user to ensure that the individual is who they claim to be.
- Enhanced Security: Authentication prevents unauthorized access by confirming the legitimacy of a user. Common authentication methods include passwords, biometrics (fingerprint or facial recognition), smart cards, and two-factor authentication (2FA).
Access Controls:
- Definition: Access controls are security measures that enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have only the permissions necessary to perform their job roles.
- Enhanced Security: Access controls limit the exposure of sensitive data and critical systems, reducing the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) or Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Definition: MFA or 2FA requires users to provide multiple forms of authentication before granting access. This typically includes something the user knows (e.g., a password) and something the user has (e.g., a mobile device).
- Enhanced Security: MFA and 2FA add an additional layer of security, making it significantly more challenging for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they possess a user's password.
Biometric Authentication:
- Definition: Biometric authentication uses unique physical or behavioral traits, such as fingerprints, facial features, or voice patterns, to verify a user's identity.
- Enhanced Security: Biometric authentication provides a high level of security because these traits are difficult to replicate or steal, making it challenging for unauthorized users to gain access.
Single Sign-On (SSO):
- Definition: SSO allows users to log in once and access multiple applications or systems without the need to enter credentials repeatedly.
- Enhanced Security: SSO enhances security by reducing the risk of password-related vulnerabilities, such as weak passwords or password reuse, and centralizing user access control.
Access Auditing and Logging:
- Definition: Access auditing and logging capture and record user activities, including login attempts, access to specific resources, and changes made to systems or data.
- Enhanced Security: Auditing and logging provide a record of user actions, facilitating security monitoring, incident detection, and forensic investigations.
Session Management:
- Definition: Session management controls monitor and manage user sessions to ensure that access is revoked after a certain period of inactivity or when a user logs out.
- Enhanced Security: Session management helps prevent unauthorized access due to unattended sessions, reducing the risk of data exposure.
Password Policies:
- Definition: Password policies enforce rules for creating and managing passwords, such as complexity requirements and password expiration.
- Enhanced Security: Strong password policies reduce the likelihood of password-related security breaches, such as brute-force attacks.
Account Lockout Mechanisms:
- Definition: Account lockout mechanisms temporarily disable accounts after a specified number of failed login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks.
- Enhanced Security: Account lockout mechanisms protect against unauthorized access by thwarting automated password-guessing attacks.
By implementing effective identification and authentication access controls, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their systems and data, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and security breaches. These controls are essential components of a robust cybersecurity strategy.