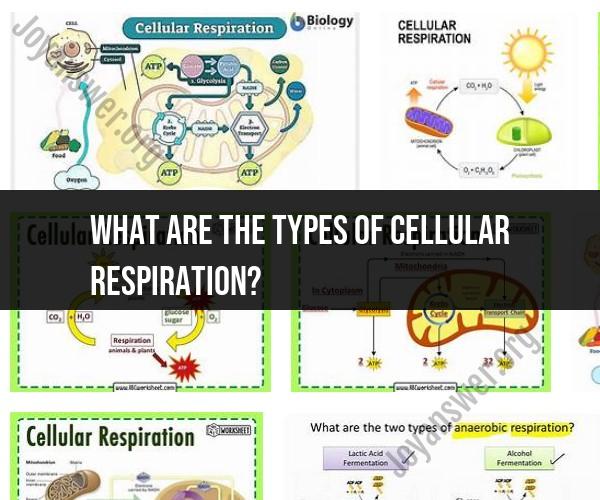
What are the types of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a biological process that occurs in various forms, depending on the presence or absence of oxygen and the specific requirements of different organisms. The two primary types of cellular respiration are aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Here's an overview of each type:
Aerobic Respiration:
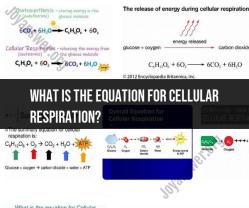
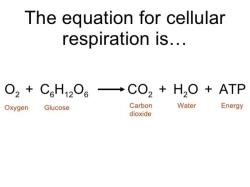
- Description: Aerobic respiration is the most efficient and common form of cellular respiration, and it occurs in the presence of oxygen. It involves the complete breakdown of glucose and other organic molecules to produce ATP, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O) as waste products.
- Stages: Aerobic respiration consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and the electron transport chain (ETC). These stages occur in mitochondria, where most of the ATP production takes place.
- Energy Yield: Aerobic respiration yields the highest amount of ATP (approximately 36-38 ATP molecules) per molecule of glucose. This is because it fully extracts energy from glucose molecules through the complete oxidation of carbon compounds.
Anaerobic Respiration:
- Description: Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen or when oxygen levels are insufficient to support aerobic respiration. It is less efficient than aerobic respiration and involves partial glucose breakdown to produce ATP and other waste products.
- Types: There are two main types of anaerobic respiration, each utilized by different organisms:
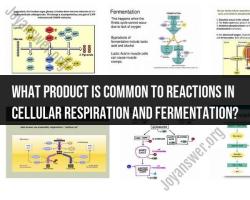
- Lactic Acid Fermentation: This type of anaerobic respiration occurs in some animal cells, including muscle cells, when oxygen is scarce. It involves the conversion of pyruvate produced in glycolysis into lactic acid. Lactic acid buildup can lead to muscle fatigue and soreness.
- Alcoholic Fermentation: Alcoholic fermentation occurs in some microorganisms like yeast and certain plant cells. It converts pyruvate into ethanol (alcohol) and CO2. This process is utilized in the production of alcoholic beverages and bread, where CO2 gas causes dough to rise.
- Energy Yield: Anaerobic respiration yields a lower amount of ATP compared to aerobic respiration. For example, glycolysis (the initial stage of both aerobic and anaerobic respiration) produces a net gain of only two ATP molecules per glucose molecule during anaerobic respiration.
Other Forms: Some organisms have adapted to specific environments and employ alternative forms of respiration. For instance, facultative anaerobes can switch between aerobic and anaerobic respiration depending on oxygen availability. Additionally, microaerophilic organisms thrive in low-oxygen environments and perform a variation of aerobic respiration with reduced oxygen requirements.
In summary, cellular respiration is essential for generating energy in the form of ATP within cells. The primary types of cellular respiration are aerobic, which occurs in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic, which occurs in the absence of oxygen or under low-oxygen conditions. Each type has distinct stages and energy yields, and they are utilized by various organisms based on their metabolic needs and environmental conditions.