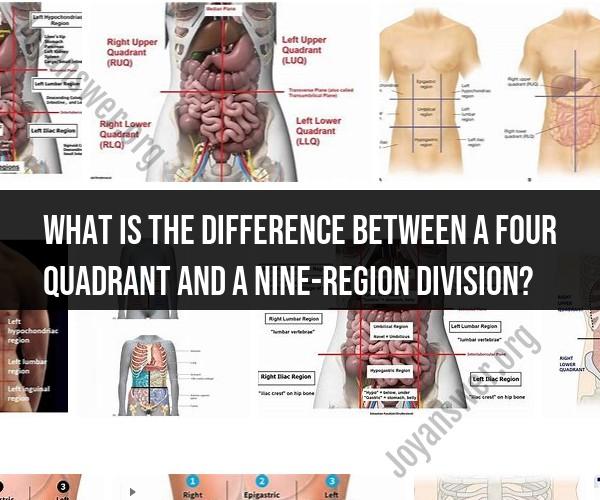
What is the difference between a four quadrant and a nine-Region Division?
A four-quadrant division and a nine-region division are both ways to divide a space or data set into distinct sections, but they differ in terms of the number of sections and their purpose. Here's an overview of the differences:
Four-Quadrant Division:
- Number of Sections: A four-quadrant division divides a space or data set into four equal sections or quadrants.
- Purpose: Four-quadrant divisions are often used to categorize data or concepts into four broad categories based on two binary criteria or dimensions. For example, in business analysis, the four quadrants may represent categories like "High Profit, High Market Share," "Low Profit, High Market Share," "High Profit, Low Market Share," and "Low Profit, Low Market Share."
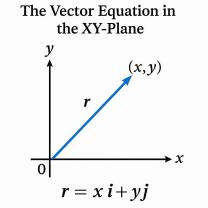
- Coordinate System: In mathematics and graphing, a four-quadrant system is often used to represent Cartesian coordinates, with the x-axis and y-axis dividing the plane into four quadrants (Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, and Quadrant IV).
Nine-Region Division:
- Number of Sections: A nine-region division divides a space or data set into nine distinct regions or sections.
- Purpose: Nine-region divisions are typically used for more detailed categorization or analysis. They can provide finer granularity than a four-quadrant division. These divisions often arise when you have three binary criteria or dimensions.
- Examples: In business, a nine-region division might be used to analyze products or strategies based on three factors like "Market Share," "Profit Margin," and "Growth Rate." This division can create categories such as "High Market Share, High Profit Margin, High Growth Rate," "Low Market Share, High Profit Margin, High Growth Rate," and so on.
In summary, the key difference between a four-quadrant and a nine-region division is the number of sections or categories they create and the level of detail in the analysis. Four-quadrant divisions are simpler and typically used for binary categorization, while nine-region divisions offer more complexity and granularity, often involving three criteria or dimensions. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the analysis or categorization you are conducting.