What do you need to know about financial statements?
Financial statements are critical documents that provide a comprehensive overview of a company's financial performance and position. They are essential for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators, as they offer insights into the financial health and stability of an organization. Here's what you need to know about financial statements:
Types of Financial Statements: There are three primary types of financial statements:
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): This statement shows a company's revenues, expenses, and net income or loss over a specific period, typically a fiscal quarter or year. It provides information about a company's profitability.
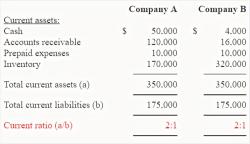
Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position): The balance sheet displays a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity at a specific point in time. It reflects the company's financial position, showing what it owns and owes.
Cash Flow Statement: This statement tracks the flow of cash into and out of a company over a given period. It is divided into operating, investing, and financing activities, providing insights into a company's liquidity and cash management.
Users of Financial Statements: Financial statements are used by various stakeholders for different purposes, including:
- Investors: Investors analyze financial statements to assess the company's potential for profitability and growth, helping them make informed investment decisions.
- Creditors: Creditors, such as banks and bondholders, use financial statements to evaluate a company's creditworthiness and ability to repay debt.
- Management: Company executives and management teams use financial statements to make strategic decisions, set financial goals, and assess performance.
- Regulators: Government agencies and regulatory bodies require companies to prepare and disclose financial statements to ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulations.
Key Components of Financial Statements:
Income Statement: It includes revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, net income, and earnings per share (EPS).
Balance Sheet: It consists of assets (current and non-current), liabilities (current and long-term), and shareholders' equity (common stock, retained earnings).
Cash Flow Statement: This statement breaks down cash flows into three categories: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities.
Accounting Principles: Financial statements are prepared following generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), depending on the country and reporting requirements.
Comparative Analysis: Financial statements are often presented with corresponding figures from previous periods to allow for year-over-year or quarter-over-quarter comparisons. These comparisons help identify trends and changes in financial performance.
Audited Statements: Many publicly traded companies and some private companies have their financial statements audited by independent auditors to provide assurance about their accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
Notes to the Financial Statements: Financial statements are usually accompanied by explanatory notes that provide additional details and explanations about specific items, accounting policies, and contingencies.
Ratio Analysis: Analysts and stakeholders use financial statements to calculate financial ratios, such as liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and leverage ratios, to assess various aspects of a company's financial health and performance.
Forward-Looking Information: While financial statements provide historical data, they do not offer predictions about future performance. Companies may issue financial forecasts and projections separately from their financial statements.
Understanding financial statements is essential for making informed investment decisions, evaluating a company's financial stability, and assessing its overall financial health. Financial literacy in interpreting these statements is valuable for both individuals and professionals in various financial and business roles.
Decoding Financial Statements: What You Need to Know
Financial statements are written records that convey the business activities and the financial performance of an entity. They are used by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to assess the financial health of a company.
The three main types of financial statements are:
- Balance sheet: A balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder's equity at a specific point in time.
- Income statement: An income statement shows a company's revenues and expenses over a period of time.
- Cash flow statement: A cash flow statement shows how much cash a company has generated and used over a period of time.
The Basics of Financial Statements: A Comprehensive Overview
Balance sheet
The balance sheet is divided into two sides: assets and liabilities plus shareholder's equity. Assets are the resources that a company owns, such as cash, inventory, and property. Liabilities are the debts that a company owes, such as accounts payable and loans. Shareholder's equity is the amount of money that the shareholders have invested in the company.
Income statement
The income statement shows a company's revenues and expenses over a period of time. Revenues are the money that a company earns from its operations. Expenses are the costs that a company incurs to generate revenue. Net income is the difference between revenues and expenses.
Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement shows how much cash a company has generated and used over a period of time. It is divided into three sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Operating activities are the activities that a company engages in to generate revenue. Investing activities are the activities that a company engages in to acquire or sell assets. Financing activities are the activities that a company engages in to raise or repay capital.
Financial Statements Unveiled: Understanding Their Significance
Financial statements are important because they provide a comprehensive overview of a company's financial health. They can be used to:
- Assess a company's profitability and liquidity.
- Identify trends in a company's performance.
- Compare a company to its peers.
- Make informed investment decisions.
Financial statements can be complex, but it is important to understand the basics so that you can make informed decisions about your investments and finances.
Here are some tips for understanding financial statements:
- Read the notes to the financial statements: The notes to the financial statements provide additional information about the company's accounting policies and financial performance.
- Compare the financial statements to previous periods: This will help you to identify trends in the company's performance.
- Compare the financial statements to the company's peers: This will help you to assess the company's performance relative to its competitors.
- If you are unsure about anything, ask a financial advisor for help.
Financial statements are an essential tool for anyone who wants to understand the financial health of a company. By taking the time to understand the basics of financial statements, you can make informed decisions about your investments and finances.