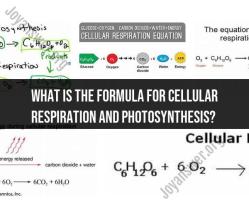
What factors influence the rate of photosynthesis?
The rate of photosynthesis, the process by which plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, is influenced by several key factors:
Light Intensity:
- Photosynthesis is directly dependent on the availability of light. As light intensity increases, the rate of photosynthesis generally increases, up to a point. Beyond a certain light intensity, called the saturation point, the rate plateaus because other limiting factors come into play.
Light Quality and Wavelength:
- Chlorophyll, the primary pigment responsible for capturing light energy, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue and red regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Green light is poorly absorbed, which is why plants appear green. Changes in the spectrum of light can affect photosynthetic rates.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Concentration:
- Carbon dioxide is one of the key reactants in photosynthesis. An increase in CO2 concentration typically leads to an increase in the rate of photosynthesis, up to a point. At very high concentrations, CO2 levels may no longer be the limiting factor.
Temperature:
- Temperature influences the rate of photosynthesis. Warmer temperatures generally lead to higher rates, within a certain range (optimal temperature varies by plant species). Too high or too low temperatures can denature enzymes and reduce photosynthetic efficiency.
Water Availability:
- Adequate water is essential for photosynthesis. Water is not only a reactant in the light reactions but also plays a role in maintaining turgor pressure in plant cells, which is necessary for the opening of stomata to allow CO2 uptake. Water stress can limit photosynthesis.
Nutrient Availability:
- Plants require various nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients, to carry out photosynthesis efficiently. Nutrient deficiencies can limit photosynthetic rates.
Oxygen Concentration:
- While oxygen is a product of photosynthesis, its concentration in the leaf's interior can influence photosynthetic rates. High oxygen concentrations can compete with CO2 for binding to the enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO), potentially leading to a decrease in photosynthesis.
Leaf Anatomy:
- Leaf structure, including the arrangement and density of chloroplasts, the number and size of stomata, and the thickness of the leaf cuticle, can influence the rate of photosynthesis.
Photosynthetic Pigments:
- The type and abundance of photosynthetic pigments, such as chlorophyll-a and chlorophyll-b, can affect the efficiency of light absorption and energy conversion.
Genetics:
- Different plant species or varieties may have genetic variations that affect their photosynthetic rates. Genetic modifications can also influence photosynthesis for specific purposes, such as crop improvement.
Pollution and Stress:
- Environmental stressors, such as air pollution or high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can negatively impact photosynthesis by damaging plant tissues or interfering with metabolic processes.
Time of Day:
- Photosynthesis generally occurs during daylight hours when there is sufficient light. At night, plants typically engage in respiration rather than photosynthesis.
CO2 Compensatory Point:
- This is the point at which the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration, resulting in no net gain in carbon. It varies with factors like temperature and light intensity.
Understanding these factors that influence the rate of photosynthesis is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices, improving crop yields, and managing ecosystems. Farmers, researchers, and conservationists take these factors into account to promote healthy plant growth and address environmental challenges.
Factors Driving Photosynthesis Rate: What You Need to Know
The rate of photosynthesis is affected by a variety of factors, including:
- Light intensity: Photosynthesis requires sunlight, so the rate of photosynthesis increases as the light intensity increases. However, there is a point where the rate of photosynthesis plateaus, as the enzymes involved in photosynthesis cannot work any faster.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: Carbon dioxide is a reactant in photosynthesis, so the rate of photosynthesis increases as the carbon dioxide concentration increases. However, there is also a point where the rate of photosynthesis plateaus, as the other factors involved in photosynthesis become limiting.
- Temperature: The enzymes involved in photosynthesis work best at a certain temperature range. If the temperature is too low or too high, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease.
- Water availability: Water is a reactant in photosynthesis, so the rate of photosynthesis will decrease if there is not enough water available.
- Nutrient availability: Plants need certain nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, to carry out photosynthesis. If these nutrients are not available, the rate of photosynthesis will decrease.
Influences on Photosynthesis: Key Determinants
In addition to the environmental factors listed above, the rate of photosynthesis can also be affected by the following factors:
- The type of plant: Different plants have different photosynthetic rates. For example, C4 plants have a higher photosynthetic rate than C3 plants in hot, dry conditions.
- The age of the plant: Younger plants typically have a higher photosynthetic rate than older plants.
- Plant health: Stressed or diseased plants typically have a lower photosynthetic rate than healthy plants.
The Science Behind Photosynthesis: Environmental Influences
The environmental factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis can interact with each other in complex ways. For example, the rate of photosynthesis is typically higher at higher temperatures, but the rate of photosynthesis will decrease if there is not enough water available. This is because plants need water to regulate their temperature and to transport nutrients and other molecules throughout the plant.
Conclusion
The rate of photosynthesis is affected by a variety of factors, both environmental and plant-specific. Understanding these factors can help us to optimize photosynthesis in crops and other plants, which can lead to increased yields and improved food security.