What energy conversion occurs in a wind turbine?
The energy conversion process in a wind turbine involves the transformation of kinetic energy from the motion of the wind into electrical energy that can be used to power homes and businesses. This conversion occurs in several key stages:
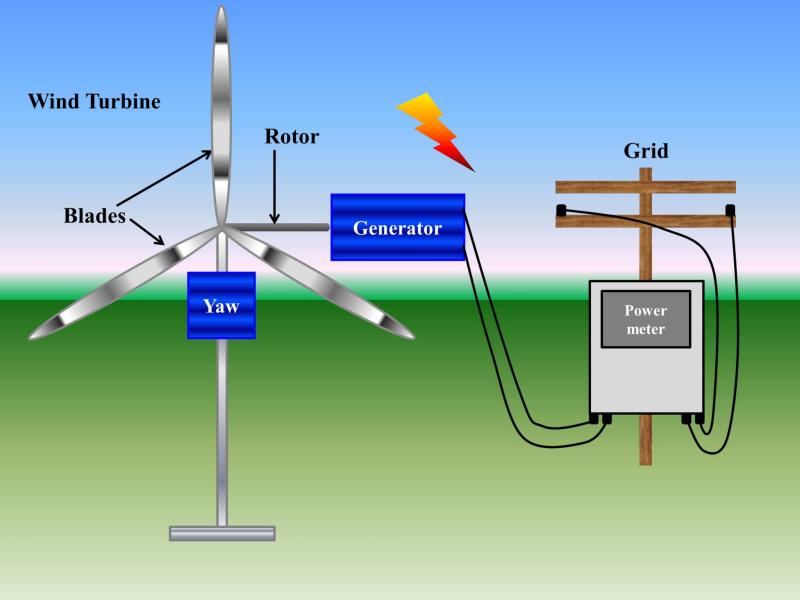
Kinetic Energy of the Wind:
- The process begins with the kinetic energy of the moving air, which is the energy associated with the motion of the wind.
Rotor Blades Capture Energy:
- The rotor blades of the wind turbine are designed to capture this kinetic energy. They are engineered to efficiently interact with the wind, creating lift and causing the blades to spin.
Rotation of the Rotor Blades:
- As the wind blows against the rotor blades, they begin to rotate. This rotation represents the conversion of kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy in the form of rotational motion.
Rotation of the Main Shaft:
- The rotor blades are connected to the main shaft of the wind turbine. As the blades rotate, they transfer their mechanical energy to the main shaft, causing it to spin.
Mechanical Energy to Electrical Energy:
- The main shaft is connected to a generator, which is the heart of the energy conversion process. The mechanical energy of the spinning shaft is transferred to the generator.
Generator Operation:
- Inside the generator, the mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through the principle of electromagnetic induction. The generator contains a rotor (rotating part) and a stator (stationary part). As the rotor spins, it creates a changing magnetic field. This changing magnetic field induces an electric current in coils of wire in the stator.
Generation of Electrical Energy:
- The electrical energy produced in the generator is typically in the form of alternating current (AC). This electrical energy is the final product of the energy conversion process within the wind turbine.
Conversion and Conditioning:
- The electrical energy generated may go through transformers and other electrical equipment to adjust its voltage and frequency to match the grid or the specific application.
Grid Connection:
- The electrical energy is then transmitted through power lines and connected to the electrical grid. It becomes part of the larger electricity supply and can be distributed and used to power homes, businesses, and industries.
Energy Storage (Optional):
- In some cases, excess energy generated by the wind turbine can be stored in batteries or other energy storage systems for use when the wind is not blowing.
Inverter (if needed):
- In cases where the wind turbine generates direct current (DC) but the grid or application requires alternating current (AC), an inverter may be used to convert the energy from DC to AC.
The entire energy conversion process in a wind turbine is highly efficient and allows the kinetic energy of the wind to be transformed into clean, renewable electrical energy. Wind power contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and diversifying the energy mix, making it an important component of sustainable and environmentally friendly energy generation.
Understanding the energy conversion process in a wind turbine
Wind turbines stand as beacons of renewable energy, gracefully harnessing the power of the wind to generate clean and usable electricity. The process of transforming wind energy into electricity involves a fascinating interplay of aerodynamic principles, mechanical motion, and electrical induction. Let's delve into the intricacies of this process and uncover how wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into usable electrical power.
Step 1: Capturing Wind Energy
The journey of wind energy to electricity begins with the interaction of wind blades with the moving air. As wind flows over the blades, it creates lift, similar to the force that keeps airplanes airborne. This lift force, acting on the blades, causes them to rotate, and this rotational motion is the key to generating electricity.
Step 2: Transferring Rotational Motion
The rotating blades, collectively known as the rotor, form the heart of a wind turbine. The rotor is typically mounted on a tall tower to capture wind at higher speeds, where the energy density is greater. As the wind turns the rotor, the rotational motion is transferred to a central shaft, which acts as the conduit for energy transfer.
Step 3: Converting Mechanical Energy to Electrical Power
At the core of the wind turbine lies the generator, the electrical counterpart to the rotor's mechanical energy. The generator is a device that converts rotational motion into electrical energy through a process called electromagnetic induction.
Electromagnetic Induction: The Key to Electricity Generation
Inside the generator, coils of wire are arranged in a specific pattern within a magnetic field. When the rotor turns, it causes the coils to rotate within the magnetic field. This movement of the coils relative to the magnetic field induces an electrical current in the wires.
Step 4: Transmission and Distribution
The electrical energy generated by the wind turbine is not directly usable in homes or businesses. It first needs to be transformed and transmitted to the power grid, which acts as a network of interconnected power lines that distribute electricity to consumers.
Step 5: Stepping Up Voltage for Transmission
Transformers are used to step up the voltage of the generated electricity, making it suitable for long-distance transmission through high-voltage power lines. These power lines carry the electricity from wind farms to substations, where it is further transformed and distributed to homes and businesses.
Efficiency of Energy Conversion in Modern Wind Turbines
Modern wind turbines have achieved remarkable efficiency in converting wind energy into electricity. The theoretical maximum efficiency for a wind turbine is known as the Betz limit, which stands at around 59.3%. While no wind turbine can reach this theoretical maximum, modern wind turbines typically achieve efficiencies between 30% and 45%.
Factors that affect the efficiency of energy conversion in wind turbines include:
Wind speed: Higher wind speeds result in greater energy capture and conversion efficiency.
Blade design: The design and shape of the blades significantly impact the turbine's ability to capture wind energy.
Generator efficiency: The efficiency of the generator plays a crucial role in converting rotational motion into electrical energy.
Aerodynamic considerations: Minimizing aerodynamic losses, such as drag and turbulence, improves the overall efficiency of the turbine.
As technology continues to advance, the efficiency of wind turbines is expected to further improve, making wind energy an even more attractive and viable source of clean, renewable energy.