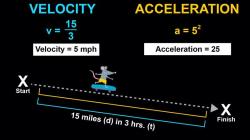
What does projectile mean in physics?
In physics, a projectile refers to an object that is thrown or projected into the air and is subject only to the force of gravity and air resistance (if applicable). The term is commonly used to describe the motion of objects such as baseballs, bullets, or launched rockets. The key characteristics of a projectile's motion include its trajectory, range, and the shape of its path.
Here are some fundamental concepts related to projectiles in physics:
Trajectory:
- The trajectory is the curved path that a projectile follows during its motion. The shape of the trajectory is influenced by the initial velocity, launch angle, and the force of gravity acting on the projectile.
Gravity:
- Gravity is the force that pulls the projectile downward toward the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity, denoted as "g," typically has a value of approximately 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s²) near the Earth's surface. Gravity affects the vertical motion of the projectile.
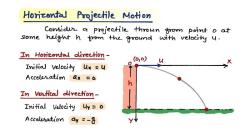
Horizontal and Vertical Components:
- The motion of a projectile can be divided into horizontal and vertical components. The horizontal motion is typically uniform (assuming no air resistance), while the vertical motion is influenced by gravity.
Launch Angle:
- The launch angle is the angle at which the projectile is initially launched with respect to the horizontal. The launch angle significantly affects the range and height of the projectile's trajectory.
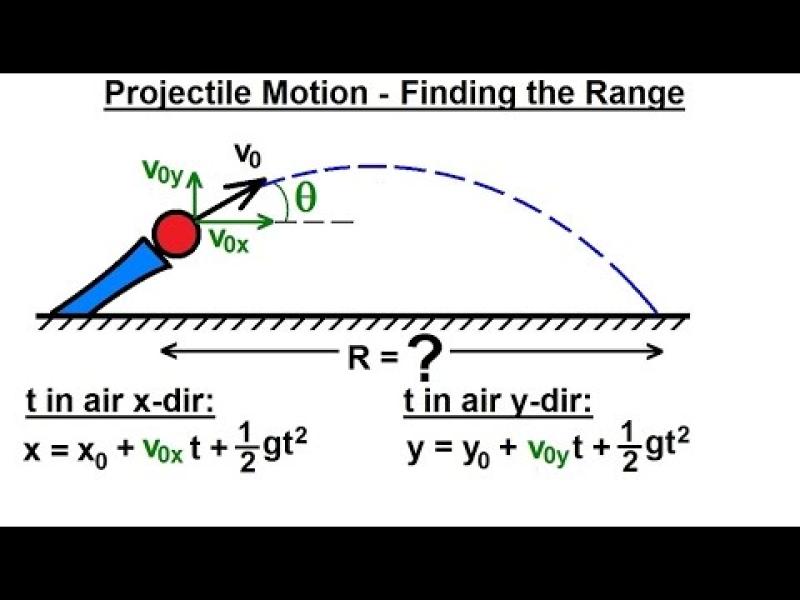
Range:
- The range of a projectile is the horizontal distance it travels before hitting the ground. The range is influenced by factors such as the initial velocity and launch angle.
Projectile Motion Equations:
The equations governing projectile motion can be derived using principles of kinematics. The horizontal and vertical motions are essentially independent, and equations describe the position, velocity, and time of the projectile.
For example, the horizontal distance traveled (range, ) can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
- is the initial velocity,
- is the launch angle,
- is the acceleration due to gravity.
Projectile motion is a classical example of two-dimensional motion in physics. It is studied to understand the behavior of objects in free fall or under the influence of a constant force (gravity) in a vacuum or near the Earth's surface. The principles of projectile motion have practical applications in fields such as physics, engineering, ballistics, and sports science.
What does projectile mean in the context of physics?
A projectile in physics is any object that is thrown or launched into the air and then moves freely under the influence of gravity. Once an object is launched, it is no longer propelled by any force other than gravity. Projectiles can be launched at any angle, but they will always follow a curved path due to the acceleration of gravity.
How is the term "projectile" defined, and what are its applications in physics?
The term "projectile" is defined as "an object thrown or shot into the air." Projectiles are used in a variety of applications in physics, including:
- Ballistics: The study of the motion of projectiles, such as bullets and rockets.
- Artillery: The use of cannons and other artillery pieces to launch projectiles at long distances.
- Aerospace engineering: The design and construction of aircraft and spacecraft, which can be considered projectiles when they are launched into space.
- Sports: Projectile motion is used in many sports, such as baseball, football, and basketball.
Are there common misconceptions or additional concepts related to projectiles?
One common misconception about projectiles is that they only move in a parabolic path. However, projectiles can actually move in a variety of paths, depending on their initial launch velocity and angle. For example, a projectile launched at a high angle will follow a more vertical path, while a projectile launched at a low angle will follow a more horizontal path.
Another additional concept related to projectiles is drag. Drag is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air. Drag is caused by the friction between the object and the air. The amount of drag on an object depends on its shape and size. For example, a baseball will experience more drag than a golf ball due to its larger surface area.
Conclusion
Projectiles are a fundamental concept in physics with a wide range of applications. By understanding the motion of projectiles, we can better understand and design many different technologies and systems.