What are the different forces in motion?
In physics, forces in motion refer to the various types of forces that can act on objects to cause them to move or change their state of motion. Understanding these forces is essential for explaining the behavior of objects in motion. Here are some of the different forces in motion:
Gravity (Weight):
- Gravity is the force that attracts two objects with mass toward each other. It is responsible for the weight of objects on Earth and the gravitational pull that keeps objects anchored to the ground. The force of gravity acts vertically downward.
Friction:
- Friction is the force that opposes the relative motion or attempted motion of two objects in contact. It can act in various directions and depends on factors such as the nature of the surfaces in contact and the force pressing them together.
Applied Force:
- An applied force is a push or pull that is applied to an object by another object or by a person. For example, pushing a book across a table or lifting a box involves applying a force.
Tension:
- Tension is the force that is transmitted through a string, cable, or rope when it is pulled tight. It acts along the length of the string and is responsible for keeping objects suspended or connected.
Normal Force:
- The normal force is the force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it. It acts perpendicular to the surface and counteracts the force of gravity.
Air Resistance (Drag):
- Air resistance, also known as drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object as it moves through a fluid, such as air or water. It depends on factors like the object's shape and speed.
Buoyant Force:
- Buoyant force is the upward force exerted by a fluid on an object submerged in the fluid. It counteracts the force of gravity and is responsible for objects floating in water.
Electromagnetic Forces:
- Electromagnetic forces include both attractive forces (e.g., magnetic attraction) and repulsive forces (e.g., electrical repulsion). These forces can affect the motion of charged particles and magnetized objects.
Torsional Force (Torque):
- Torsional force, also known as torque, is a force that causes an object to rotate about an axis. It is often associated with the twisting of objects, such as a wrench turning a bolt.
Spring Force:
- Spring force is exerted by a compressed or stretched spring when it tries to return to its equilibrium position. It can be either a compressive force or a tensile force, depending on the direction of deformation.
Centripetal Force:
- Centripetal force is directed toward the center of rotation and keeps an object moving in a circular path. It is essential for circular motion and is provided by various forces, such as tension or gravity.
Magnetic Force:
- Magnetic force is the force of attraction or repulsion between magnetic objects or charged particles in motion. It plays a crucial role in the behavior of magnets and magnetic materials.
Nuclear Forces:
- Nuclear forces are strong forces that act within the nucleus of an atom to hold protons and neutrons together. These forces are responsible for the stability of atomic nuclei.
These are some of the fundamental forces in motion that play a role in the behavior of objects in the physical world. Understanding how these forces interact and affect the motion of objects is a fundamental aspect of classical mechanics and physics.
Forces in Motion: An Overview of the Various Types
A force is any push or pull that acts on an object. It can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. There are many different types of forces, but they can be broadly categorized into two types: contact forces and non-contact forces.
Contact forces are forces that act when two objects are in contact with each other. Some examples of contact forces include:
- Friction: Friction is a force that opposes the motion of two surfaces sliding against each other.
- Tension: Tension is a force that is transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight.
- Normal force: The normal force is the force that a surface exerts on an object that is resting on it.
Non-contact forces are forces that act on an object at a distance. Some examples of non-contact forces include:
- Gravity: Gravity is a force that attracts any two objects with mass.
- Magnetism: Magnetism is a force that attracts or repels objects with magnetic properties.
- Electromagnetism: Electromagnetism is a force that acts between electrically charged objects.
Unraveling Motion Forces: Understanding Their Diversity
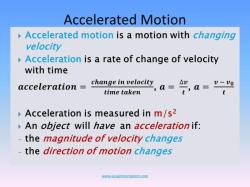
The diversity of forces in motion is due to the many different ways that forces can interact with objects. For example, a force can cause an object to accelerate, decelerate, change direction, or deform.
The effect of a force on an object depends on a number of factors, including the magnitude of the force, the direction of the force, and the mass of the object.
For example, a larger force will cause an object to accelerate more than a smaller force. A force acting in the opposite direction to the motion of an object will cause the object to decelerate. And a more massive object will be more difficult to accelerate than a less massive object.
Dynamics in Action: Exploring Different Forces in Motion
Here are some examples of how different forces can affect motion:
- Gravity: Gravity causes objects to fall to the ground. It also causes planets to orbit the sun and moons to orbit planets.
- Friction: Friction opposes the motion of two surfaces sliding against each other. This is why it is difficult to push a heavy object across a rough surface.
- Tension: Tension is used to operate many different devices, such as bows and arrows, slingshots, and fishing poles.
- Normal force: The normal force prevents objects from falling through the ground. It also allows us to walk and run without slipping.
- Magnetism: Magnets are used in many different devices, such as compasses, electric motors, and speakers.
- Electromagnetism: Electromagnetism is used in many different devices, such as generators, motors, and transformers.
Forces in motion are essential to our understanding of the world around us. They explain why objects move the way they do and how we can control their motion.