What is the difference between ratio and rate?
Ratio:
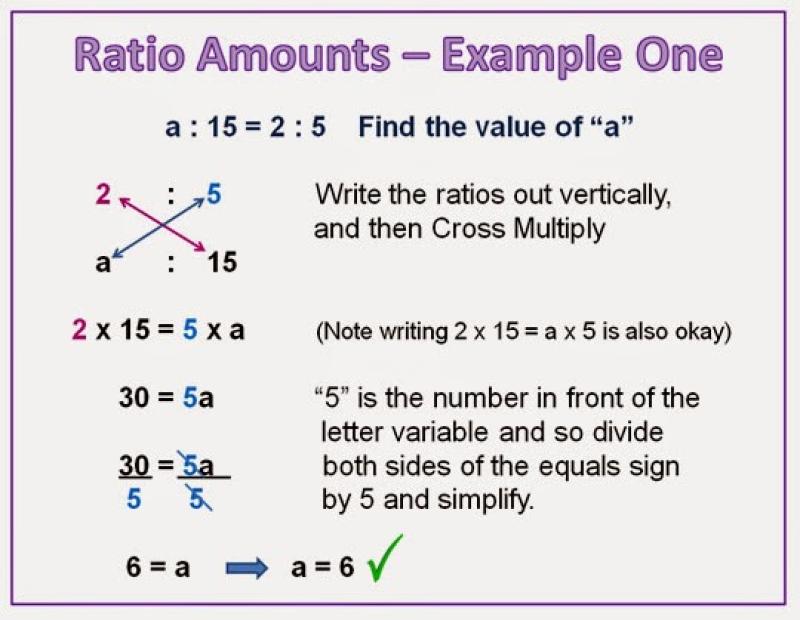
Definition: A ratio is a comparison of two quantities. It represents the relative size of one quantity compared to another. The ratio of two numbers and is often expressed as , where and are the terms of the ratio.
Example: If you have 3 red balls and 5 blue balls, the ratio of red balls to blue balls is .
Properties: Ratios can be simplified, multiplied, and divided, but they do not involve a specific unit of measurement. Ratios are often used to represent relationships between different parts of a whole.
Rate:
Definition: A rate is a special type of ratio that involves the comparison of two quantities with different units. It expresses how one quantity changes in relation to another.
Formula: The general formula for a rate is:
Example: If a car travels 60 miles in 2 hours, the rate of speed is .
Key Differences:
Units:
- Ratios do not involve specific units of measurement. They represent a relationship between quantities, but the units are not specified.
- Rates involve the comparison of two quantities with different units. The units are an integral part of the rate.
Representation:
- Ratios are typically represented as or .
- Rates are expressed as a quantity per unit, often written as .
Application:
- Ratios are commonly used to compare parts to a whole or parts to each other within the same unit.
- Rates are used to express the relationship between quantities with different units, often involving a change over time.
Example:
- In the example of red and blue balls, the ratio is , representing a comparison between two quantities of the same kind.
- In the example of the car's speed, the rate is , representing a comparison between distance and time, involving different units.
In summary, while both ratio and rate involve the comparison of quantities, the key distinction lies in the inclusion of units. Ratios are unitless and compare quantities within the same unit, while rates involve quantities with different units and are expressed as a quantity per unit.
1. Understanding the Concepts of Ratios and Rates
Ratios and rates are fundamental concepts in mathematics that represent relationships between quantities. They are used to compare, measure, and analyze various aspects of the world around us.
Ratios
A ratio is a comparison of two or more quantities of the same kind. It is expressed as a quotient or fraction, with no units. For example, the ratio of men to women in a room could be 3:2, indicating that there are three men for every two women.
Rates
A rate is a ratio that involves a change in a quantity over time or distance. It is expressed as a quotient with units that reflect the change. For instance, the speed of a car could be 60 miles per hour (60 mph), indicating that it covers 60 miles in one hour.
2. Distinguishing Ratios from Rates
The key distinction between ratios and