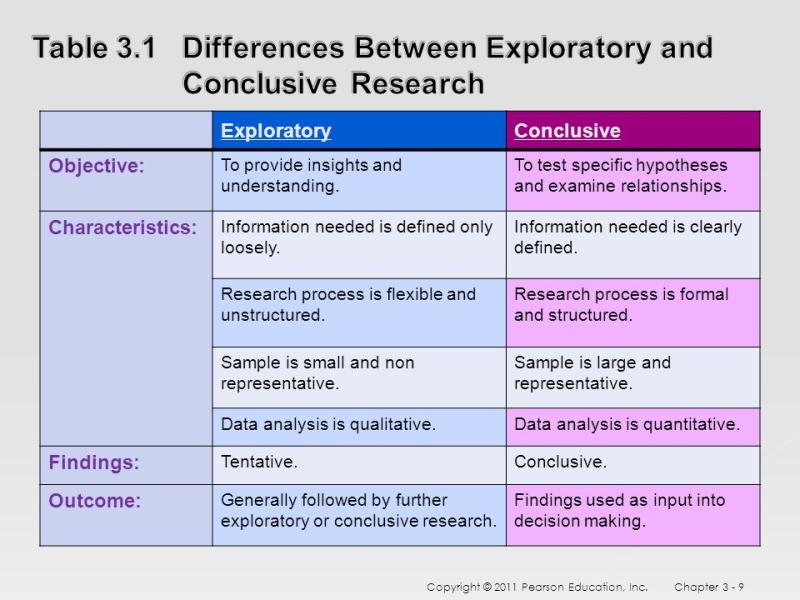
What is the difference between technical and business writing?
Technical writing and business writing are two distinct genres of writing, each serving specific purposes within professional contexts. While there is some overlap, they differ in terms of their focus, audience, and communication goals. Here are key variances between technical and business writing:
Technical Writing:
Focus:
- Purpose: Technical writing is primarily focused on providing detailed, specialized information about a technical subject. It is often used to explain complex processes, procedures, or concepts.
- Content: Technical writing is heavy on technical details, specifications, and instructions. It is designed to convey information to a specific audience with a deep understanding of the subject matter.
Audience:
- Specialized Audience: The audience for technical writing consists of individuals with a specific technical background or expertise. This could include engineers, scientists, IT professionals, or others with specialized knowledge.
Language:
- Specialized Terminology: Technical writing often includes specialized terminology and jargon that is specific to the field. The language used is precise and technical, catering to the expertise of the audience.
Format:
- Structured and Formal: Technical documents are often highly structured and follow a formal format. They may include sections such as abstracts, methodologies, results, and conclusions.
Visual Elements:
- Diagrams and Illustrations: Technical writing frequently incorporates diagrams, charts, and illustrations to enhance understanding. Visual elements are used to clarify complex information.
Examples:
- User Manuals: Technical writing is commonly found in user manuals, product documentation, engineering reports, scientific papers, and other documents that explain technical processes.
Business Writing:
Focus:
- Purpose: Business writing is focused on facilitating communication within a business context. It aims to convey information clearly, build relationships, and achieve specific business goals.
- Content: Business writing covers a broad range of documents, including emails, memos, reports, proposals, and business plans. The content may relate to various aspects of business, such as marketing, management, finance, or human resources.
Audience:
- Diverse Audience: The audience for business writing can be diverse and may include individuals within and outside the organization. It could range from employees and managers to clients, customers, or other stakeholders.
Language:
- Accessible Language: Business writing uses language that is accessible to a general audience. While it may include industry-specific terms, it avoids excessive jargon and aims for clarity and simplicity.
Format:
- Varied Formats: Business writing can take on various formats, depending on the purpose and audience. It may include formal reports, informal emails, business letters, marketing materials, and more.
Visual Elements:
- Supportive Graphics: While not as technical as in technical writing, business writing may include graphics, charts, or visuals to support and emphasize key points. Visual elements are used to enhance readability and engagement.
Examples:
- Email Correspondence: Business writing is evident in everyday email communication, business proposals, business plans, executive summaries, marketing materials, and other documents used in a business context.
In summary, while both technical and business writing share the goal of effective communication, they differ in their focus, audience, and the depth of technical detail. Technical writing delves deeply into specialized subjects for a knowledgeable audience, while business writing is more varied and addresses a broader audience within the context of business and organizational communication.
Distinguishing features between technical and business writing styles
Both technical and business writing aim to convey information effectively, but they do so in distinct ways to cater to different audiences and objectives. Here are some key features that distinguish them:
Audience:
- Technical writing: Targets individuals with specific technical knowledge or expertise in a given field. The writer needs to tailor the language and explanations to the audience's level of understanding.
- Business writing: Aims at a broader audience, often within an organization or a specific industry. The writer needs to consider diverse backgrounds and ensure clarity for non-technical readers.
Purpose:
- Technical writing: Provides instructions, explains complex processes, and presents technical information in a clear and concise way. Focuses on accuracy and comprehensiveness to enable readers to perform tasks or understand technical concepts.
- Business writing: Persuades, informs, and builds relationships. It aims to convince readers to take action, make decisions, or understand business concepts. Persuasiveness and engagement are key aspects.
Content and Style:
- Technical writing: Uses precise terminology, jargon, and specific details relevant to the technical field. Often features charts, diagrams, and other visual aids to explain complex concepts. Focuses on objective reporting and factual information.
- Business writing: Uses clear and concise language avoiding technical jargon unless necessary. Prioritizes active voice and storytelling elements to engage the reader. May use persuasive language and appeals to emotions to achieve desired outcomes.
Structure and Tone:
- Technical writing: Follows a logical and structured format, often with step-by-step instructions, numbered lists, and clearly defined sections. Maintains a neutral and objective tone throughout.
- Business writing: Can be more flexible in structure, depending on the purpose. Often uses introductions, conclusions, and transitions to guide the reader. The tone can vary depending on the audience and purpose, from formal and informative to persuasive and engaging.
Overall:
- Technical writing: Focuses on accuracy, clarity, and comprehensiveness in presenting technical information for a specific audience with existing knowledge in the field.
- Business writing: Focuses on persuasion, engagement, and relationship building to convey business information and achieve desired outcomes within a broader audience.
While distinctions exist, some overlap can occur, especially in fields where technical topics need to be explained to a non-technical audience. The key is to understand the audience, purpose, and desired outcome to choose the appropriate style and effectively communicate your message.
I hope this helps clarify the key differences between technical and business writing styles! Feel free to ask if you have any further questions or want to explore specific examples in different contexts.