What is mass, weight, volume and density?
Demystifying Mass, Weight, Volume, and Density: Key Differences and Interconnections
Understanding the distinctions between mass, weight, volume, and density is fundamental in physics and everyday life. These concepts are interrelated and play a crucial role in various scientific and practical applications.
1. Mass:
Definition: Mass is the amount of matter in an object and is typically measured in kilograms (kg) or grams (g).
Key Points:
- Mass is an intrinsic property and remains constant regardless of an object's location.
- It can be measured using a balance or scale.
- Mass is often used in scientific calculations, including determining an object's density.
2. Weight:
Definition: Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity and is typically measured in newtons (N) or pounds (lb).
Key Points:
- Weight depends on both an object's mass and the strength of the gravitational field it's in.
- Weight can vary depending on the location; for instance, an object weighs less on the moon than on Earth.
- The formula for weight is: Weight (N) = Mass (kg) × Acceleration due to Gravity (m/s²).
3. Volume:
Definition: Volume is the amount of space occupied by an object and is usually measured in cubic meters (m³) or liters (L).
Key Points:
- Volume is a measure of the physical size or capacity of an object.
- It is often determined by measuring length, width, and height (for regular shapes) or by fluid displacement (for irregular shapes).
- Volume is used to calculate density and to quantify the amount of a substance in a given space.
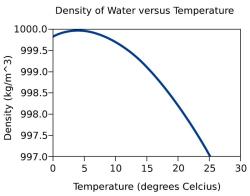
4. Density:
Definition: Density is the mass per unit volume of an object and is typically expressed in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
Key Points:
- Density reflects how closely packed the particles or molecules are within a substance.
- It is calculated using the formula: Density (kg/m³) = Mass (kg) ÷ Volume (m³).
- Objects with higher density are typically heavier for their size.
Interconnections:
- Mass and volume are essential components in calculating density. An object with a given mass but a smaller volume will have a higher density.
- Weight depends on both mass and the strength of gravity. An object with the same mass will weigh less on the moon, where gravity is weaker, compared to Earth.
- Volume is often used in practical applications to determine the amount of a substance needed, such as calculating the volume of a liquid in a container or the size of a room.
In summary, mass and weight represent different aspects of an object's characteristics, with weight being the force due to gravity acting on mass. Volume is the measure of an object's physical space, while density describes how tightly packed the matter within an object is. Understanding these concepts and their interconnections is vital for physics, engineering, and everyday problem-solving.