What do you know about forces and motion?
Forces and motion are fundamental concepts in physics that describe how objects interact with each other and how they move. Here is a basic overview of these concepts:
Forces:
Definition: A force is a push or pull exerted on an object due to the interaction with another object. Forces can cause objects to change their motion, speed, or direction.
Units: The standard unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) is the newton (N). One newton is the force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass by one meter per second squared.
Types of Forces:
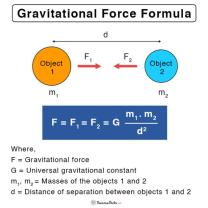
- Gravity: The force of attraction between two masses, such as the force that keeps objects on Earth's surface.
- Friction: The force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact with each other.
- Tension: The force exerted by a stretched or pulled object, like a rope or a cable.
- Normal Force: The force exerted by a surface to support the weight of an object resting on it.
- Applied Force: A force applied to an object by a person or another object.
- Spring Force: The force exerted by a compressed or stretched spring.
- Electromagnetic Forces: Forces associated with electric charges and magnets.
Motion:
Definition: Motion refers to the change in an object's position concerning a reference point or frame of reference. It can involve changes in speed, direction, or both.
Key Concepts:
- Distance: The total length of the path traveled by an object.
- Displacement: The change in an object's position from the initial point to the final point, including direction.
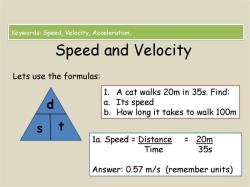
- Speed: The rate of change of distance with respect to time. It is a scalar quantity (only magnitude).
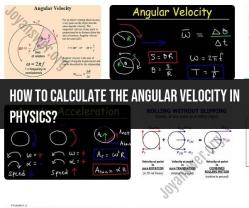
- Velocity: The rate of change of displacement with respect to time. It is a vector quantity (magnitude and direction).
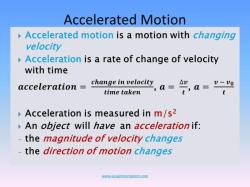
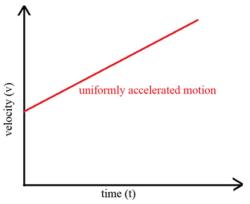
- Acceleration: The rate of change of velocity with respect to time. It can be positive (speeding up), negative (slowing down), or changing direction.
- Inertia: The tendency of an object to resist changes in its state of motion. It is related to an object's mass.
- Newton's Laws of Motion: A set of three fundamental principles formulated by Sir Isaac Newton that describe the relationship between forces and motion.
Newton's Laws of Motion:
First Law (Law of Inertia): An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force.
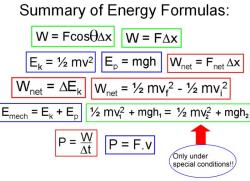
Second Law (F = ma): The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. F = ma, where F is the net force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
Third Law (Action-Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When one object exerts a force on another, the second object exerts an equal force in the opposite direction.
These principles govern the behavior of objects in the presence of forces and are essential for understanding the mechanics of everyday objects and celestial bodies in the universe.
Forces and Motion: A Comprehensive Overview
Forces and motion are two fundamental concepts in physics. Force is defined as any push or pull that acts on an object. Motion is defined as a change in position over time.
Forces and motion are related by Newton's second law of motion, which states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This means that the more force applied to an object, or the less mass it has, the greater its acceleration will be.
There are four fundamental forces in nature: gravity, electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. Gravity is the force that attracts all objects with mass. Electromagnetism is the force that attracts or repels charged particles. The strong nuclear force holds together the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The weak nuclear force is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay.
Forces can be classified as either contact forces or non-contact forces. Contact forces are forces that act between two objects that are touching. Examples of contact forces include friction, tension, and normal force. Non-contact forces are forces that act between two objects that are not touching. Examples of non-contact forces include gravity and electromagnetism.
Exploring the World of Physics: Forces and Motion Basics
Forces and motion are at play all around us, from the simple act of walking to the complex motion of the planets and stars.
When we walk, we apply a force to the ground with our feet. This force propels us forward. The ground applies a force back on our feet, which is called friction. Friction opposes our motion, but it also helps us to maintain traction and prevents us from slipping.
When we throw a ball, we apply a force to the ball with our hand. This force causes the ball to accelerate. The ball continues to move forward until it is stopped by gravity or air friction.
Gravity is a force that attracts all objects with mass. The more mass an object has, the stronger the gravitational force on it. Gravity is what keeps us on the ground and what causes the planets to orbit the sun.
Electromagnetism is a force that attracts or repels charged particles. Like charges repel, while opposite charges attract. Electromagnetism is responsible for many phenomena in nature, such as lightning and magnetism.
Physics Fundamentals: What You Should Know about Forces and Motion
Here are some fundamental concepts about forces and motion that everyone should know:
- Forces can cause objects to change their velocity, which is a measure of speed and direction.
- The net force on an object is the sum of all the forces acting on it.
- Newton's second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass.
- There are four fundamental forces in nature: gravity, electromagnetism, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force.
- Forces can be classified as either contact forces or non-contact forces.
Forces and motion are essential concepts in physics, and they play a role in many aspects of our everyday lives. By understanding the basics of forces and motion, we can better understand the world around us.