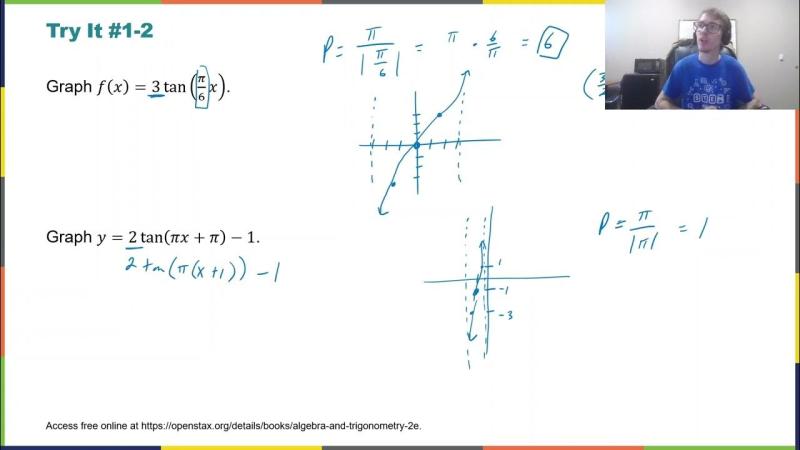
What are the types of trigonometric functions?
Trigonometric functions are mathematical functions that relate angles of a right triangle to the ratios of the sides of the triangle. There are several fundamental trigonometric functions, each with its own unique properties. The primary trigonometric functions are:
Sine Function (sin θ):
- In a right triangle, the sine of an angle () is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
- Formula:
Cosine Function (cos θ):
- The cosine of an angle () is the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse.
- Formula:
Tangent Function (tan θ):
- The tangent of an angle () is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the adjacent side.
- Formula:
Cosecant Function (csc θ):
- The cosecant of an angle () is the reciprocal of the sine. It is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the side opposite the angle.
- Formula:
Secant Function (sec θ):
- The secant of an angle () is the reciprocal of the cosine. It is the ratio of the hypotenuse to the adjacent side.
- Formula:
Cotangent Function (cot θ):
- The cotangent of an angle () is the reciprocal of the tangent. It is the ratio of the adjacent side to the side opposite the angle.
- Formula:
These functions are fundamental in trigonometry and have applications in various branches of mathematics, physics, engineering, and other scientific fields. They are often used to describe and analyze periodic phenomena, such as waveforms and oscillations.
It's worth noting that these functions can also be defined using the unit circle and have mathematical properties that extend beyond right triangles. Trigonometric functions play a crucial role in solving equations involving triangles and understanding the geometry of angles and rotations.
Sure, I can help you with that.
1. Varieties or classifications of trigonometric functions
Trigonometric functions are a set of mathematical functions that relate the angles of a triangle to its sides. They are essential tools in trigonometry, geometry, and calculus.
What different types of trigonometric functions exist in mathematics?
The six most common trigonometric functions are:
Sine (sin): The ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Cosine (cos): The ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse of a right triangle.
Tangent (tan): The ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side of a right triangle.
Cotangent (cot): The reciprocal of the tangent function.
Secant (sec): The reciprocal of the cosine function.
Cosecant (csc): The reciprocal of the sine function.
Are there specialized forms or variations within trigonometric functions?
Yes, there are specialized forms or variations within trigonometric functions. Some of these include:
Inverse trigonometric functions: These functions are the inverse of the standard trigonometric functions. They are used to find the angle when given the side of a triangle.
Hyperbolic trigonometric functions: These functions are similar to trigonometric functions, but they are defined with the hyperbolic sine function instead of the sine function.
Complex trigonometric functions: These functions are defined using complex numbers. They are used in a variety of applications, including signal processing and circuit analysis.
I hope this helps!