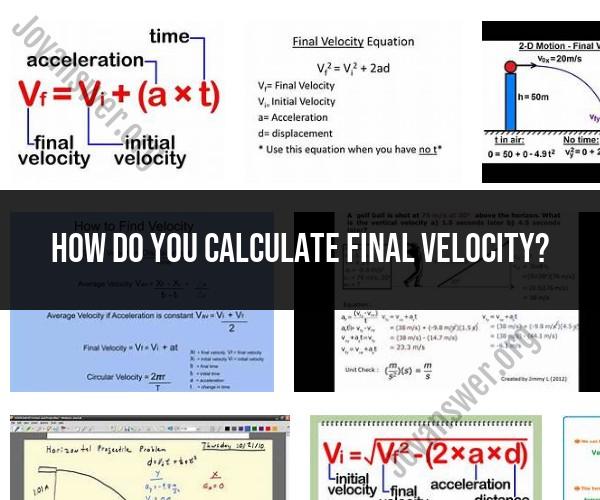
How do you calculate final velocity?
To calculate the final velocity of an object in physics, you can use the following formula:
Where:
- represents the final velocity (in meters per second, m/s).
- represents the initial velocity (in meters per second, m/s).
- represents the acceleration of the object (in meters per second squared, m/s²).
- represents the time interval during which the acceleration occurs (in seconds, s).
Here's how to use the formula step by step:
Identify the values you have:
- The initial velocity () of the object.
- The acceleration () acting on the object.
- The time interval () during which the acceleration occurs.
Plug these values into the formula and perform the calculations:
Calculate the product of acceleration () and time ().
Add the result from step 3 to the initial velocity () to find the final velocity ().
The final velocity is the velocity of the object at the end of the time interval after undergoing acceleration. Make sure to use consistent units (e.g., meters per second for velocity, meters per second squared for acceleration, and seconds for time) to ensure that your final velocity is in the correct units.
Final velocity (also known as ) can be calculated using the following formula in physics:
Where:
- is the final velocity (the velocity at the end of the motion).
- is the initial velocity (the velocity at the beginning of the motion).
- is the acceleration of the object.
- is the time period over which the velocity changes.
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how to use this formula to calculate the final velocity of an object:
Determine Initial Values: Identify the values of the initial velocity (), acceleration (), and time () that are relevant to the problem or scenario you are working with. Make sure these values are in consistent units (e.g., meters per second for velocity, meters per second squared for acceleration, and seconds for time).
Plug into the Formula: Insert these values into the formula .
Calculate: Perform the arithmetic operations according to the formula. Multiply the acceleration () by the time () and then add the result to the initial velocity ().
Final Velocity: The result of this calculation will be the final velocity () of the object. Be sure to include the appropriate units in your answer.
It's important to note that this formula assumes constant acceleration over the given time period. If acceleration is not constant, more complex equations and techniques may be required to calculate the final velocity. However, for many basic physics problems involving constant acceleration, this formula is sufficient.
Here's a practical example:
Example: A car accelerates from rest () at a rate of for a time of . What is the final velocity of the car?
Using the formula :
So, the final velocity of the car is .