What are economic principles?
Economic principles, also known as economic concepts or economic fundamentals, are foundational ideas and theories that form the basis for understanding how economies work. These principles provide a framework for analyzing and interpreting economic phenomena, making informed decisions, and studying the behavior of individuals, businesses, and governments in economic systems. Here are some key economic principles:
Scarcity: Scarcity is the fundamental economic problem that arises from limited resources and unlimited wants. It's the idea that resources, such as time, money, and natural resources, are finite, and people must make choices about how to allocate these resources to satisfy their needs and wants.
Supply and Demand: The law of supply and demand describes how prices are determined in a market economy. It states that the price of a good or service will tend to rise when demand exceeds supply and fall when supply exceeds demand. This principle influences pricing, production, and consumer choices.
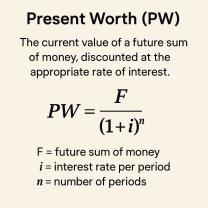
Opportunity Cost: Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that must be forgone when a choice is made. It highlights the trade-offs individuals and businesses face when allocating resources. Decisions involve comparing the benefits of one option to the benefits of the next best alternative.
Marginal Analysis: Marginal analysis involves examining the incremental or additional costs and benefits of a decision. Rational decision-makers often compare the marginal cost of an action to the marginal benefit to determine if it's worthwhile.
Gains from Trade: This principle suggests that individuals and nations can benefit from specialization and trade. When individuals or countries focus on producing what they are relatively more efficient at and trade with others, both parties can enjoy a higher standard of living.
Competition: Competition is a driving force in market economies. It encourages efficiency, innovation, and the delivery of goods and services that meet consumer preferences. Competitive markets tend to allocate resources efficiently.
Government Intervention: Government plays a role in economic systems through policies, regulations, taxation, and public spending. The extent and nature of government intervention vary across different economic systems (e.g., capitalism, socialism, mixed economies).
Incentives: Economic agents respond to incentives. Changes in prices, wages, taxes, or regulations can influence behavior. Positive incentives encourage desired actions, while negative incentives discourage unwanted behaviors.
Utility: Utility refers to the satisfaction or well-being individuals derive from consuming goods and services. Economic decisions are often driven by the pursuit of maximizing utility, given resource constraints.
Elasticity: Price elasticity and income elasticity are concepts that measure the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of a good or service to changes in price or income, respectively. Understanding elasticity helps firms and policymakers make pricing and taxation decisions.
These economic principles provide a framework for analyzing economic issues, making predictions, and guiding economic policies. Economists use them to develop models and theories that help explain and predict economic behavior and outcomes. Moreover, individuals can apply these principles in their daily lives when making choices about spending, saving, investing, and more.