What are the basic genetics?
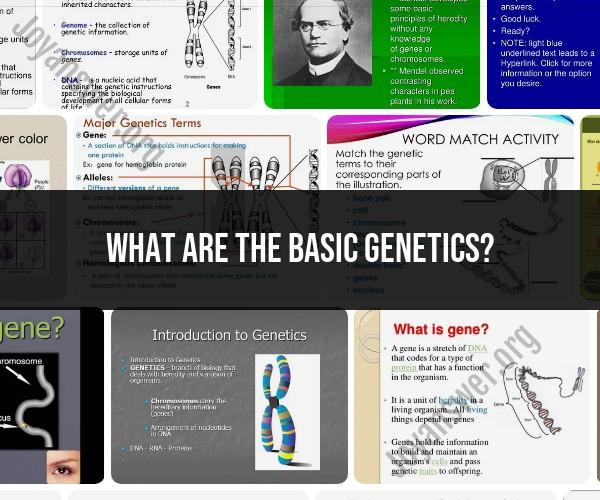
Basic genetics encompasses fundamental concepts and principles related to the inheritance and transmission of genetic traits from one generation to the next. These concepts serve as the foundation for understanding genetic variation, heredity, and how genes play a role in the characteristics of living organisms. Here are some essential genetic concepts:
Genes: Genes are segments of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that contain instructions for building and maintaining an organism's cells and structures. Each gene carries information for a specific trait, such as eye color or blood type.
Alleles: Alleles are different versions or variations of a gene. They can result in different traits or characteristics. For example, there are alleles for blue eyes and alleles for brown eyes.
Genotype: Genotype refers to an organism's genetic makeup, or the specific combination of alleles it carries for a particular trait. Genotypes can be homozygous (two identical alleles) or heterozygous (two different alleles).
Phenotype: Phenotype is the observable physical or biochemical trait that results from an organism's genotype. It is what you can see or measure, such as eye color, hair texture, or height.
Dominant and Recessive Traits: Some alleles are dominant, meaning their presence masks the expression of the corresponding recessive allele. Recessive alleles are expressed only when two copies are present (homozygous recessive).
Mendelian Inheritance: Mendelian genetics, based on the work of Gregor Mendel, describes the inheritance of traits controlled by single genes with clear dominant and recessive alleles. Mendel's laws, including the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, explain how genes are inherited.
Punnett Squares: Punnett squares are diagrams used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of their parents. They are helpful tools for understanding genetic inheritance.
Genetic Crosses: Genetic crosses involve breeding organisms with specific genotypes to study the inheritance of traits. Common types include monohybrid crosses (involving one trait) and dihybrid crosses (involving two traits).
Genetic Disorders: Genetic disorders are conditions caused by mutations or abnormalities in an individual's DNA. These disorders can be inherited from one's parents and can affect health and development.
Chromosomes: Chromosomes are thread-like structures found in the cell nucleus that carry genes. Humans have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs, with one chromosome in each pair inherited from each parent.
Sexual Reproduction: Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material from two parents to create offspring with a unique combination of genes. This contributes to genetic diversity within populations.
Mutation: A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of a gene. Mutations can lead to new genetic variations and are a source of genetic diversity in populations.
These are some of the core concepts in basic genetics. Understanding these principles is crucial for comprehending how traits are inherited, how genetic variation occurs, and how genetic information is passed from one generation to the next in all living organisms, including humans. Genetics plays a fundamental role in biology and has applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.