How to identify arcs and central angles?
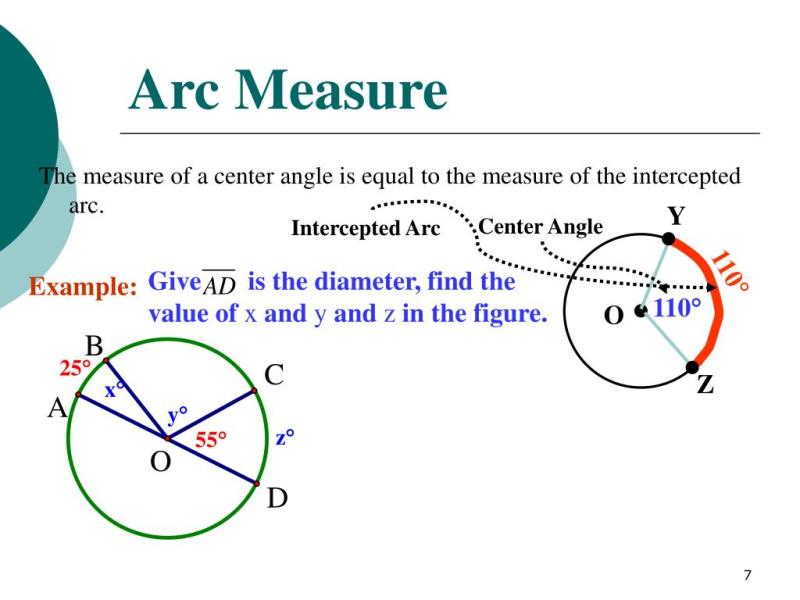
In geometry, an arc is a portion of the circumference of a circle, and a central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle. Central angles are associated with arcs in a way that the measure of the central angle is equal to the measure of the intercepted arc. Here's how to identify arcs and central angles:
Identifying Arcs:
Understand Circumference:
- The circumference of a circle is the distance around its boundary.
Recognize Arcs:
- An arc is a part of the circumference. It can be a small portion or the entire circumference.
Naming Arcs:
- Arcs are often named using three points: the two endpoints and a point on the arc. For example, if points A and B define an arc, it can be denoted as arc AB.
Major and Minor Arcs:
- An arc that is less than half the circumference is a minor arc. An arc that is more than half the circumference is a major arc.
Identifying Central Angles:
Understand Central Angles:
- A central angle is an angle formed by two radii (lines from the center of the circle to any two points on its circumference).
Vertex at the Center:
- The vertex of a central angle is always at the center of the circle.
Measure of Central Angles:
- The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the intercepted arc.
Naming Central Angles:
- Central angles are often named using three points: the center of the circle, and two points on the angle. For example, if the center is O and points A and B define the central angle, it can be denoted as ∠AOB.
Steps to Identify Arcs and Central Angles:
Locate the Center:
- Identify the center of the circle.
Find Arc Endpoints:
- Locate the endpoints of the arc. These points will be on the circle.
Measure Arc:
- Measure the length of the arc using appropriate units.
Identify Central Angle:
- If a central angle is associated with the arc, identify the vertex at the center of the circle and the two rays forming the angle.
Measure Central Angle:
- Measure the central angle. The measure of the central angle should match the measure of the intercepted arc.
Understanding the relationship between arcs and central angles is essential for solving problems related to circles and angles in geometry. Practice with different examples can enhance your ability to identify and work with arcs and central angles.
How to distinguish between arcs and central angles?
Arcs and central angles are two closely related concepts in geometry. An arc is a portion of a circle's circumference, while a central angle is an angle formed by two radii of a circle that meet at the center of the circle. The two terms are often used interchangeably, but there are some key differences between them.
Arcs are measured in degrees or radians. The measure of an arc is the ratio of the arc's central angle to 360 degrees (or 2π radians). For example, a semicircle has an arc measure of 180 degrees, while a full circle has an arc measure of 360 degrees.
Central angles are measured in degrees or radians. The measure of a central angle is the angle itself. For example, a right central angle has a measure of 90 degrees, while a straight central angle has a measure of 180 degrees.
What defines arcs and central angles within geometric figures?
Arcs: An arc is a portion of a circle's circumference. It is defined by two endpoints, and it can be measured in degrees or radians. The measure of an arc is the ratio of the arc's central angle to 360 degrees (or 2π radians).
Central angles: A central angle is an angle formed by two radii of a circle that meet at the center of the circle. It is defined by its vertex (the center of the circle) and its two sides (the radii). The measure of a central angle is the angle itself.
Are there visual cues or characteristics to identify arcs and central angles?
Yes, there are a few visual cues that can help you to identify arcs and central angles.
Arcs are always curved lines. They are part of the circumference of a circle.
Central angles are always formed by two radii of a circle. They meet at the center of the circle.
The vertex of a central angle is always the center of the circle.
In addition to these visual cues, you can also use the following rules to identify arcs and central angles:
An arc is always named by its endpoints. For example, the arc from point A to point B is called arc AB.
A central angle is always named by its vertex and its two sides. For example, the central angle with vertex C and sides CA and CB is called angle ACB.
I hope this helps!